Machine learning (ML) and computer vision teams face a bottleneck when preparing large ground-truth video datasets for training their models.
Because a single hour of video footage can generate over 100,000 frames, each requiring precise, temporally consistent labeling.
So the choice of video annotation tools can make or break the efficiency, cost, and quality of your vision projects.
In this article, we will provide an in-depth view of top video data annotation tools, plus a decision list to help you decide which vision platform is the best fit for your team’s needs.
If you are building computer vision models and want to accelerate your vision pipeline with high-quality training data, then try Unitlab AI. We offer AI-assisted data annotation and video annotation (coming soon), dataset versioning, and seamless collaboration.
Try Unitlab AI for free to see how it can accelerate your annotation workflow by 15x.
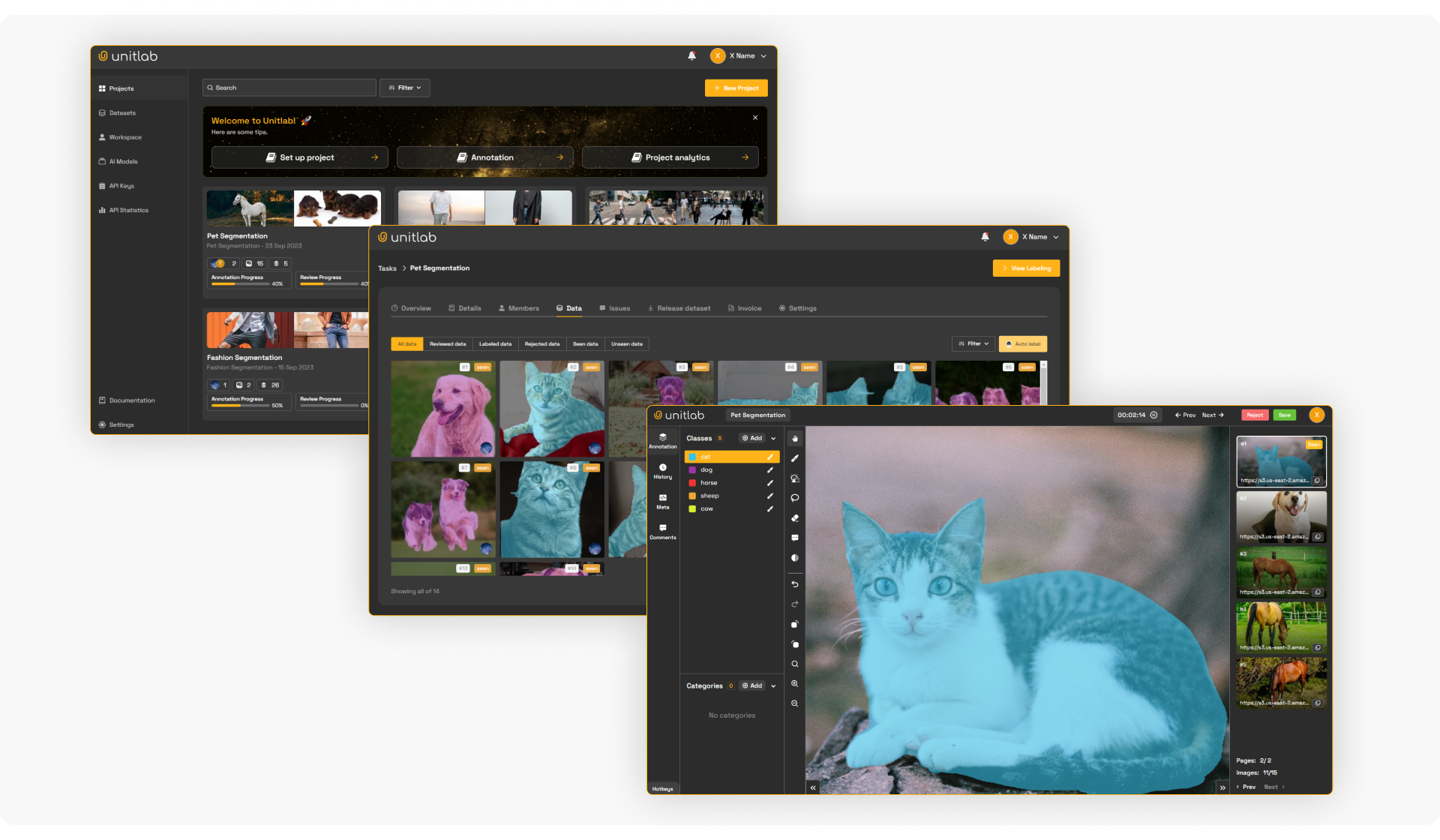
What Is a Video Annotation?
Video annotation is the process of labeling objects, actions, and events in video frames to create training data for machine learning models.
Unlike image annotation, which works with static frames, video annotation keeps temporal information like how objects move, change, and interact over time.
The output of the video annotation process is a labeled dataset in which each frame or sequence contains information about what appears in the scene, where it is located (using coordinates), and what it is doing (through classification or event tags).
That ground-truth data then enables AI models to learn to identify and track objects in new, unseen videos and help build applications from autonomous vehicles to medical diagnostics.
Video Data Annotation Types
The annotation method depends on the downstream computer vision task you're working on. So, before we go into the details, let’s take a quick look at the different types of video annotations.
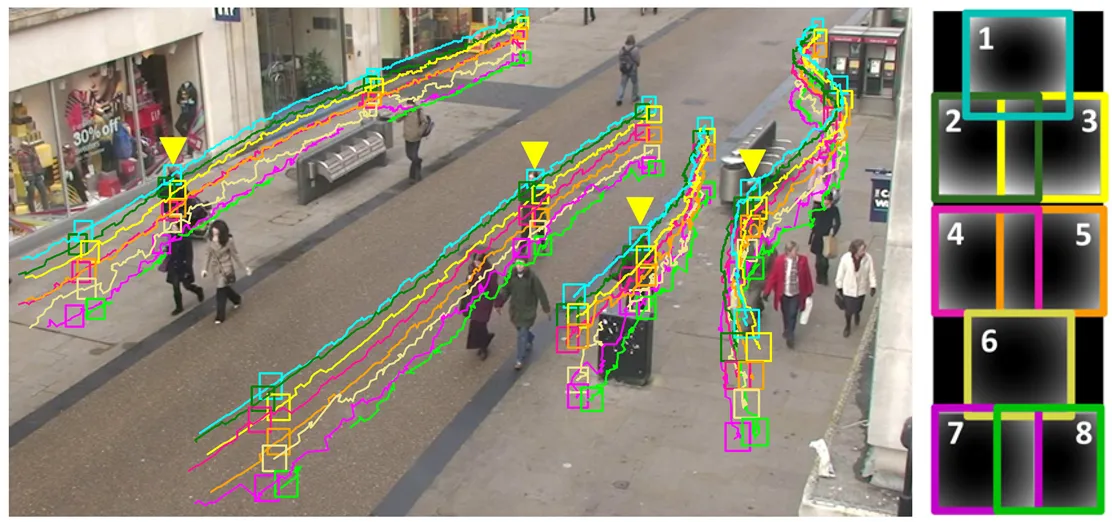
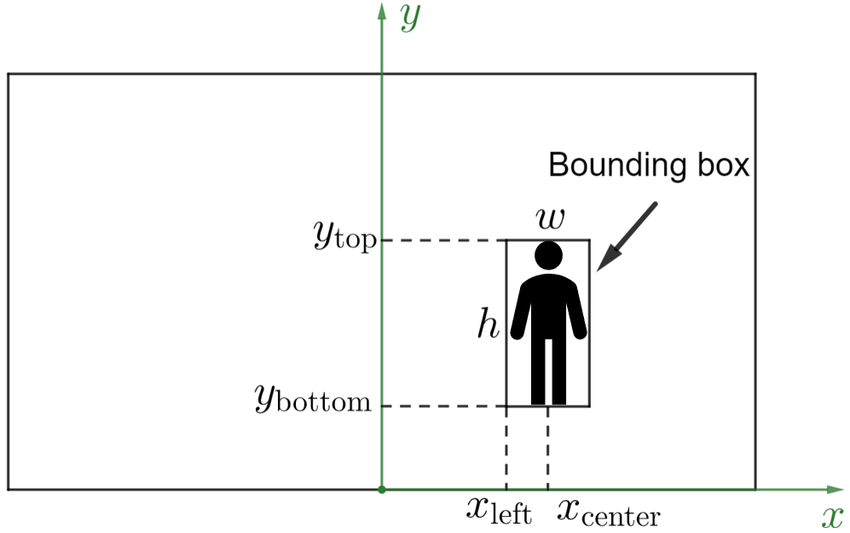
Bounding Boxes + Object Tracking (Persistent IDs)
Bounding boxes are 2D rectangular frames that annotators draw around objects in video frames. Each box defines an object's position using x, y coordinates for the top-left and bottom-right corners.
In video annotation, annotators assign persistent object IDs to track the same object across multiple frames
For example, in autonomous driving datasets, a car entering at frame 10 might receive ID Vehicle:5. That ID follows the car through occlusions, turns, and lighting changes until it exits the frame.
Polygons and Segmentation (Instance and Semantic)
Instance segmentation identifies each distinct object of interest and delineates its exact boundaries using a polygon.
Importantly, it distinguishes between individual instances of the same class (separating "BlueBerry 1" from "BlueBerry 2" in a crowded Berries).
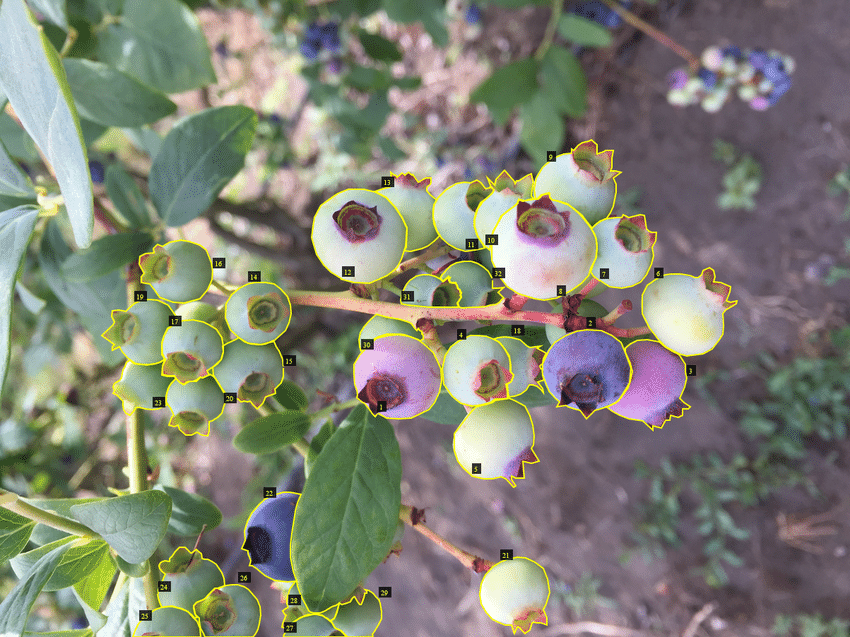

In the video annotation, these polygonal masks must be tracked and morphed frame-by-frame to match the object's deformation.
Semantic segmentation assigns a class label to every pixel in a frame. It does not distinguish between individual objects of the same class, all car pixels are simply labeled "BlueBerry."

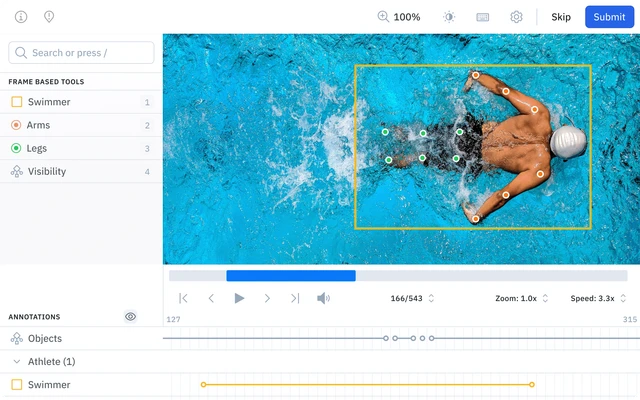
Keypoints, Pose and Landmarks
Keypoints, also known as landmark or skeletal annotation, involve placing points on specific semantic parts of an object to define its structure, posture, or orientation.
Annotators place dots on specific joints (elbows, knees, shoulders) or facial features (eyes, nose, mouth).
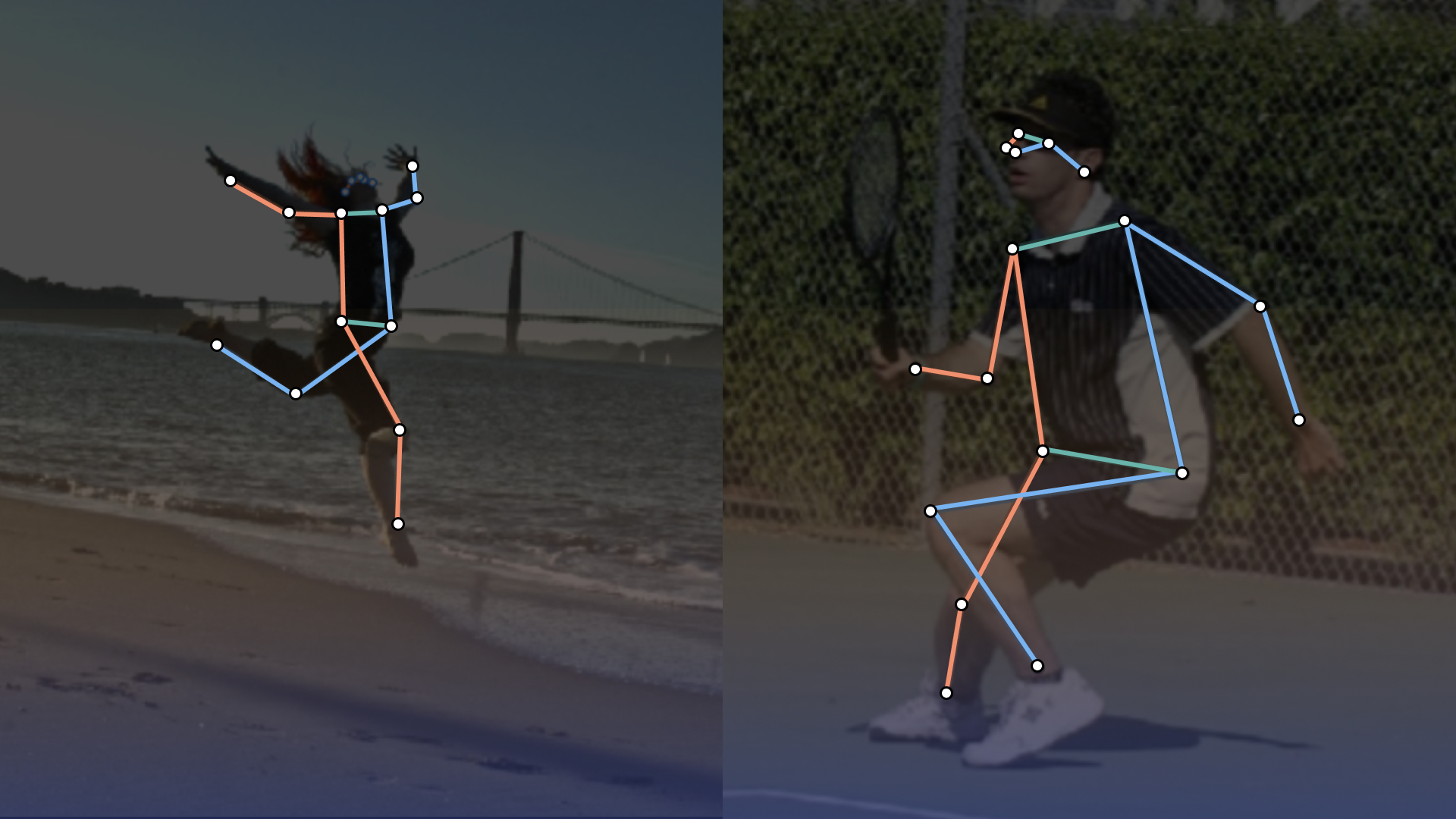

For example, in sports analytics, annotators mark athlete positions frame-by-frame to analyze movement patterns.
Similarly, in medical applications, keypoints track surgical tools or anatomical landmarks during procedures.
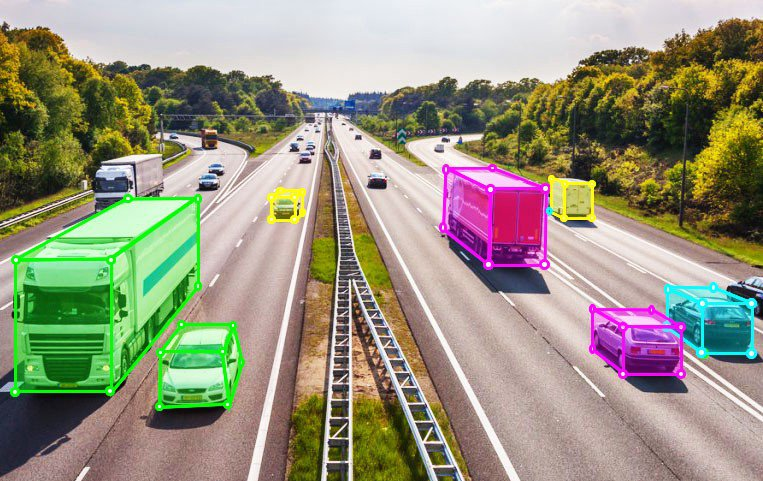
3D Cuboids
Three-dimensional bounding boxes (cuboids) represent objects in 3D space, capturing height, width, depth, and orientation.
Autonomous vehicle datasets use 3D cuboids to label cars, trucks, and obstacles, and provide the spatial information needed for path planning and collision avoidance.

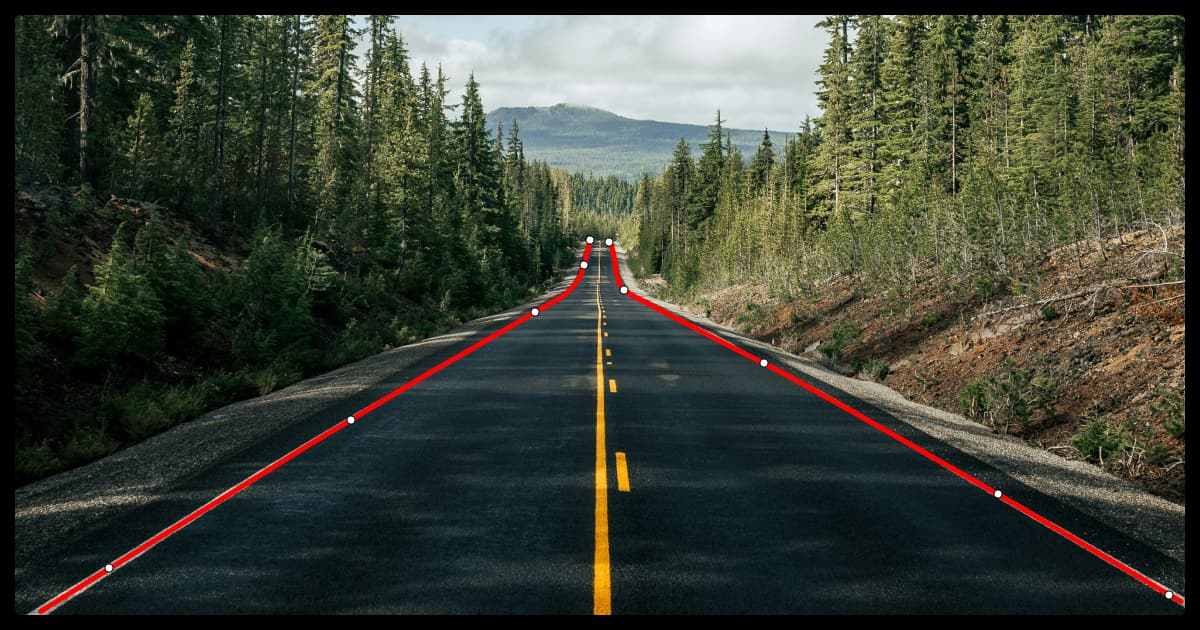
Polylines
Polylines are open shapes consisting of connected vertices (lines) used to annotate linear structures that do not form a closed loop, like road lanes, railway tracks, or pathways.
Lane detection models in autonomous driving rely on polyline annotations to find drivable areas, lane boundaries, and road markings.

Event Tagging and Temporal Segmentation
Event annotation marks specific actions, interactions, or conditions within video timeframes. Annotators tag moments when events occur, like a person waving, a traffic light turning red, or rain detected.
Simply put, event tags describe what is happening in the scene.
Now, let's look at some features you need to consider when searching for a video annotation tool.
What to Look for in Video Annotation Tools (Key Features to Consider)
Evaluate video annotation tools based on the following features when selecting a video annotation tool, so that your team can produce a high-quality dataset efficiently.
- AI-Assisted Labeling and Automation: Look for video annotation tools that integrate active learning and foundation models like Segment Anything 3 (SAM 3) or YOLO. These tools should include a magic feature that, when an annotator hovers over an object, automatically creates a tight outline or box around it. Also, auto annotation should be able to pre-label entire video sequences, so annotators mainly check the labels instead of creating them from scratch.
- Robust Object Tracking and Interpolation: Manual frame-by-frame labeling is too expensive. A good video annotation tool must support interpolation, either linear or bicubic, where you label a start and end frame, and the software automatically fills in the frames in between. Also, the tool should be able to lock onto an object (object tracking) in Frame 1 and autonomously track it through occlusion, lighting changes, and rotation for hundreds of frames without losing the persistent ID (object's identity).
- Multimodal Sensor Fusion: For advanced computer vision applications, video is rarely the only data source. The best video annotation tools combine different sensors and allow annotators to see and label 2D video frames alongside 3D LiDAR point clouds, RADAR data, or audio signals. This helps ensure that a pedestrian seen in the video matches the correct cluster of points in the LiDAR scan.
- Dataset Management and Versioning: Video annotation tools should work like a "Data Engine" with version control similar to Git. You should be able to create different versions of datasets, save changes, go back to earlier versions, and track the lineage of every label. It ensures that if a model performs poorly (or isn’t working), you can trace the issue back to the specific version of the training data used.
- Quality Assurance (QA) Workflows: Look for built-in QA pipelines that support "Consensus" (assigning the same video to multiple annotators to calculate agreement scores) and "Gold Sets" (hidden test tasks to measure annotator accuracy). The tool should also let reviewers reject certain frames or objects and send comments to fix them.
- Collaboration and Team Management: The video annotation tools should have detailed access controls so that different roles, like annotators, reviewers, and managers, can be managed easily.
- Native Video Rendering and Format Support: Many older tools treat video as a collection of images, which can cause synchronization issues and dropped frames. Modern tools use native video playback to provide accurate frame timing. The tool should support various codecs and formats like MP4, MOV, and WEBM, and be able to handle high-resolution 4K and high-frame-rate 60fps+ videos smoothly without slowing down in the browser.
- Customizable Ontologies and Attributes: The best video annotation tool should let you organize data into categories that can be nested, like Vehicle > Car > SUV. It should also support changing attributes over time, such as a Car being "Parked" in frames 1-50 and "Moving" in frames 51-100. Having flexible management of these categories is important to really understand video data.
- Integration Ecosystem (API and SDK): The annotation tool needs a strong Python SDK and REST API so it can connect with your MLOps system. You should be able to upload data automatically from cloud storage services like AWS S3, GCS, or Azure, export labels in common formats such as COCO or JSON, and start training processes easily.
- Data Security and Compliance: For enterprise use cases, security is non-negotiable, so ensure the video annotation platform is SOC 2 Type II compliant, GDPR/CCPA ready, and supports Single Sign-On (SSO). For highly sensitive data, such as in healthcare, defense, look for options to deploy the tool on-premises or within a virtual private cloud (VPC).
Best Video Annotation Tools
Let's discuss each video annotation tool in detail, compare them across key dimensions, and see how they meet the needs of CV projects.
And if you are short on time, here’s a table summarizing the main differences.
Unitlab
Unitlab AI is an AI-powered data annotation platform built for fast, high-quality dataset creation for computer vision and machine learning workflows.
Its video annotation tool (available soon) covers the standard capabilities for production video data labeling, while keeping the workflow efficient and consistent across large volumes of video frames.
Unitlab AI video data annotation includes interpolation to reduce repetitive labeling across frames, and the object tracking keeps labels consistent over time. And the object timeline view feature manages and reviews how labeled objects behave throughout a sequence.
It also supports exact frame extraction so teams can precisely select the right video frames for labeling and downstream model training. Plus SAM3 model integration speeds up tasks like segmentation and AI-assisted labeling.
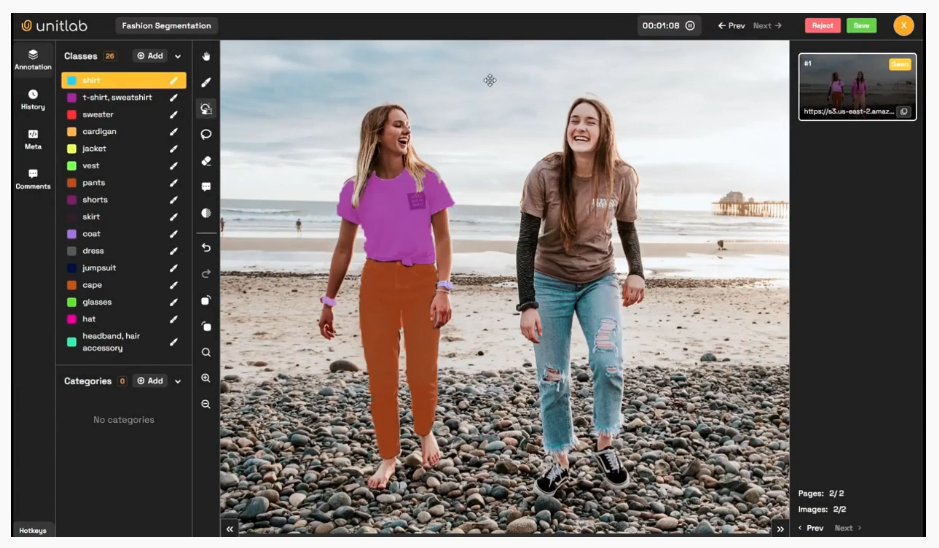
Key Features:
- Auto-annotation using SAM and proprietary models for segmentation and detection of objects and other items in video frames.
- Object tracking to maintain consistent object identity through time
- Object timeline to visualize, adjust, and QA labels across the full video sequence
- Advanced team management, real-time statistics, and role assignments
- Bring Your Own Model (BYO) integration to pre-label datasets
- Full support for secure, local deployment (on-premises) for sensitive data projects
Pros:
- Highly competitive pricing models (5x cheaper) compared to other enterprise tools.
- Focus on automation and greatly reduce the cost-per-label (15x faster).
- Modern and user-friendly interface for non-technical teams
- Supports both self-managed teams and managed labeling services (flexibility)
Cons:
- Video annotation is rolling out soon, which is a good opportunity to align early workflows with your internal labeling standards and provide feedback while the feature set is fresh.
- No dedicated mobile app for annotation management is currently available, but desktop apps are provided.
- Free: 3 Members, Unlimited Projects
- Active: $99/month for 5 Members
- Pro: $195/month for 10 Members
- Enterprise: Custom solutions
Best For: Startups, ML Engineers, and Enterprises looking for a unified, automated, and budget-friendly platform that scales with their video needs. Also, for teams working on autonomous vehicles, medical imaging, robotics, and security applications that require enterprise-grade compliance.
CVAT (Computer Vision Annotation Tool)
CVAT is open open-source data annotation tool for computer vision. It supports video formats including .mp4, .avi, and .mov, with native features for bounding boxes, polygons, skeletons, and keyframe interpolation.
CVAT excels at persistent object ID tracking across long video sequences, and that is ideal for autonomous driving and surveillance datasets.
It also includes manual and automatic QA workflows, ground truth jobs, honey pot tasks for quality validation, and integrations with AI models for model-assisted labeling.
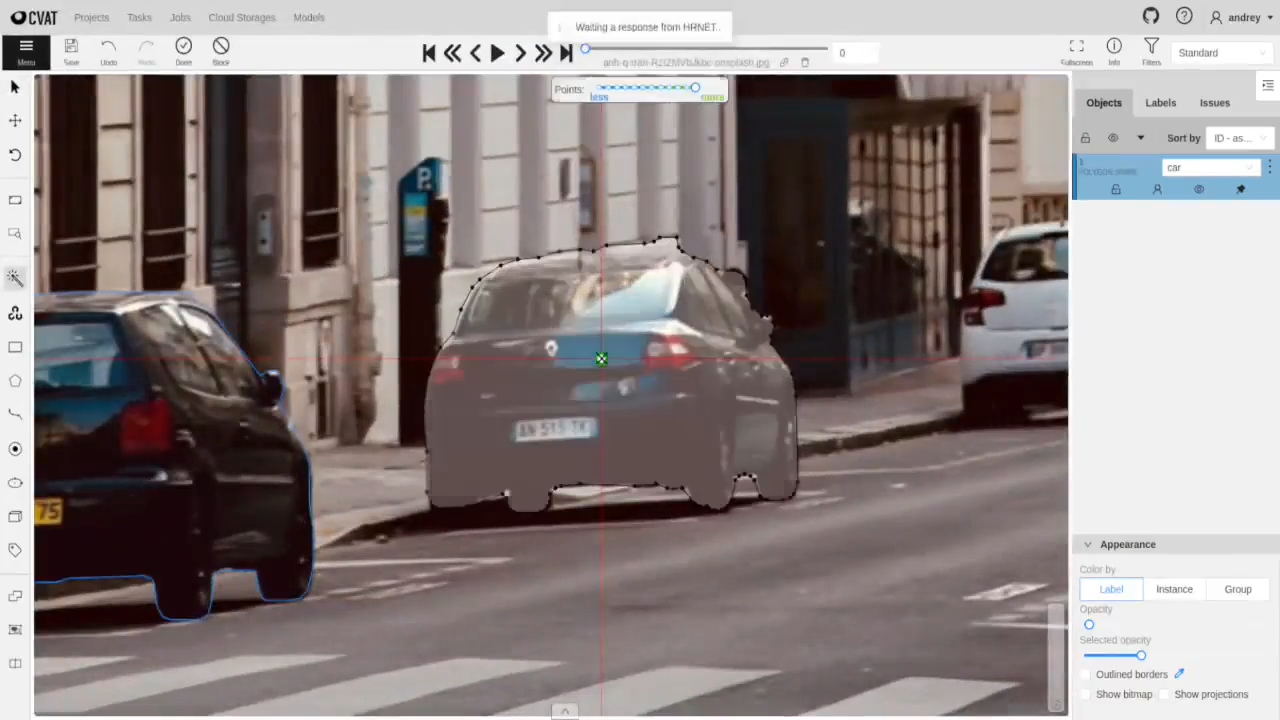
Key Features:
- Open-source with self-hosted control
- Native video support with interpolation and persistent IDs
- Ground truth jobs and honey pot QA
- Hugging Face and Roboflow integrations
- Task management and annotation versioning
Pros:
- Free tier for small teams (1-2 users)
- Full control over data and infrastructure (self-hosted)
- Strong community support on GitHub and Discord
- Stable performance on long videos
Cons:
- Requires DevOps and MLOps expertise for enterprise deployment
- UI is less polished than commercial tools
- Free: 1-2 members, community support
- Solo: $23/month (annual) or $33/month (monthly)
- Team: $23-33/user/month, depending on billing
- Enterprise (self-hosted): Starting at $12,000/year
Best For: Technical teams needing customizable pipelines, projects with privacy or infrastructure constraints, and teams with in-house DevOps support.
Encord
Encord is a data annotation platform optimized for computer vision teams working with temporal data. It uses native video rendering that preserves temporal context and reduces storage requirements.
Encord's keyframe interpolation system uses the Meta SAM for automatic object tracking across frames, even during occlusions.
It supports bounding boxes, polygons, rotatable boxes, keypoints, semantic segmentation, panoptic segmentation, and audio annotation.
Encord's timeline interface provides granular control over video sequences with frame-by-frame navigation, multi-view annotation, and temporal context visualization.
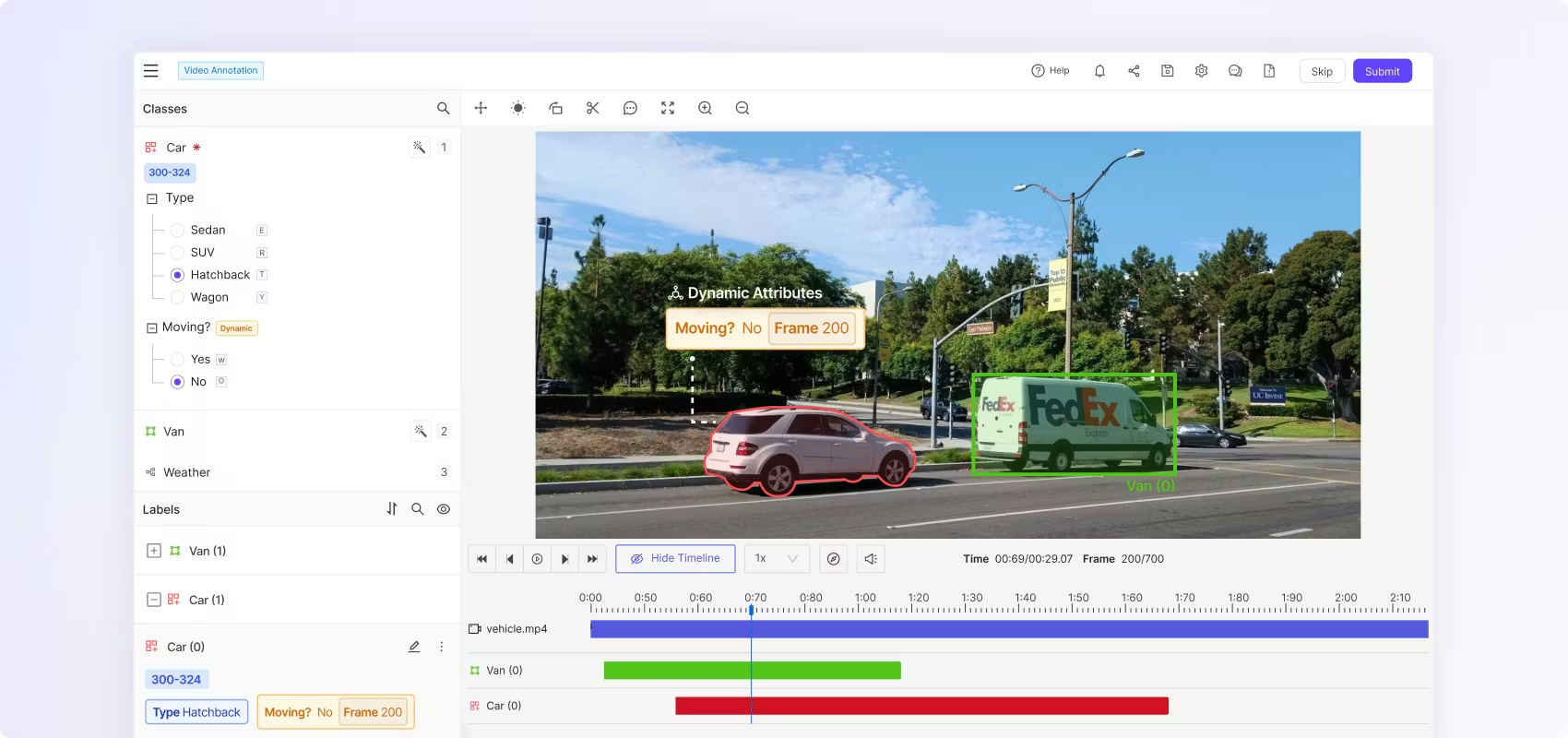
Key Features:
- Native video rendering (not frame-based)
- Active learning for intelligent frame selection
- Temporal context visualization
- Multi-view and related object annotation
- Private cloud and on-premises deployment
Pros:
- 6x faster annotation speed (claim)
- Handles long sequences without performance lag
- Strong security and compliance (SOC 2, HIPAA, GDPR)
- Purpose-built for video (native rendering)
Cons:
- Premium pricing (enterprise-focused)
- Less suitable for occasional and small projects
Pricing: Custom pricing based on team size, data volume, and support level. Contact Encord sales for quotes.
Best For: Computer vision teams working on applications requiring native video support, temporal context preservation, and enterprise-grade compliance.
V7 (Darwin)
V7 (Darwin) combines a highly responsive, modern interface with powerful Auto-Annotate features that help with complex segmentation tasks.
Auto-annotate tool segments objects across video frames with minimal interaction, automatically handling tracking and deformation.
V7 supports complex workflows where data is routed through multiple stages of annotation and review. It is strong in scientific and industrial use cases that support formats from standard video to microscopy and multi-spectral imaging.
Its dataset management acts as a visual database that lets teams query and filter data visually.
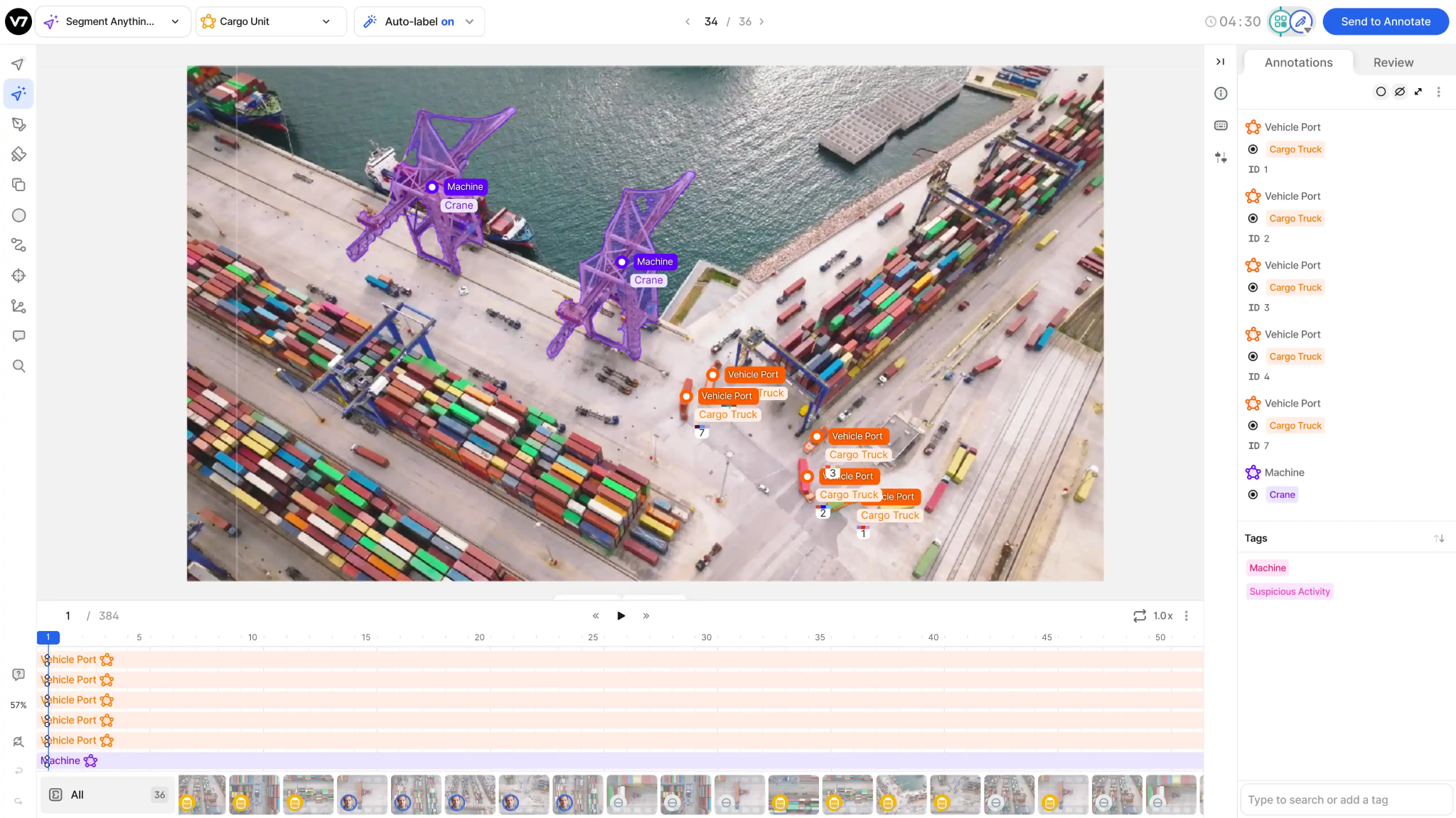
Key Features:
- Native video rendering with custom frame rates
- Auto-Track with SAM for object tracking
- Interpolation and AI-assisted labeling
- All video formats and resolutions are supported
- Comprehensive API for automation
Pros:
- Transparent, usage-based pricing
- Strong automation features
- Flexible workflows and customization
- API-first design for ML pipelines
Cons:
- Premium pricing structure
- Limited customization vs open-source tools
Pricing: Custom pricing = Platform fee + User licenses + Data processing volume. The Starter plan is about $9,000/year (50K files, 3 seats, 1 workspace). Contact V7 for tailored quotes.
Best For: AI teams building custom annotation workflows, organizations needing API-first platforms for automation, and projects requiring managed annotation services alongside tool access.
SuperAnnotate
SuperAnnotate video annotation tool handles formats including MP4, AVI, MOV, FLV, MPEG, and WEBM with features like auto-track, frame interpolation, and frame-by-frame labeling.
It integrates Meta's SAM for pixel-perfect segmentation and offers model-assisted annotation to accelerate workflows.
SuperAnnotate supports both tool-only purchases for internal teams and all-in-one services, including managed annotation, project management, and MLOps support.
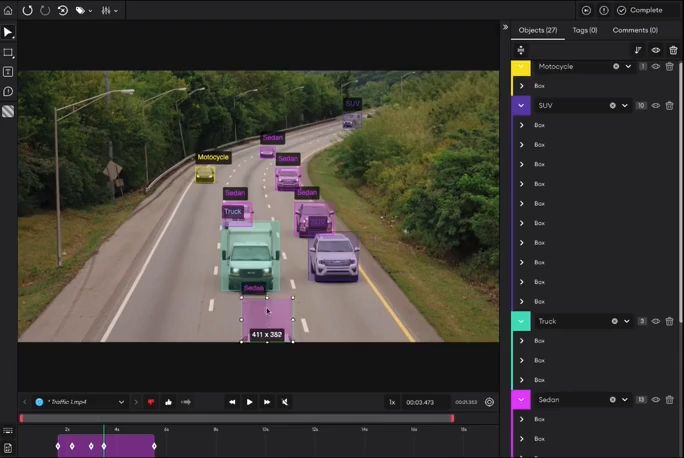
Key Features:
- Auto-track and interpolation for video
- Workforce marketplace (400+ annotation teams)
- Model-assisted labeling
- Python SDK and API access
Pros:
- Access to managed annotation workforce (WForce)
- Multi-modal capabilities in a single platform
- Flexible pricing (tool-only or full-service)
Cons:
- Smaller open-source community than CVAT
- Custom pricing can be expensive for small teams
Pricing: Custom pricing based on users, data volume, and service level.
Best For: Organizations needing multi-modal annotation (video + text + audio), teams requiring access to managed annotation workforces, and enterprises with complex MLOps needs.
Labelbox
Labelbox is another data annotation platform with native video support designed for high-volume labeling workflows.
It uses a timeline-based editor that preserves video context and lets annotators create per-frame and global classifications, bounding boxes, polygons, keypoints, and segmentation masks.
Model-assisted labeling integrates foundation models and custom AI to pre-label frames, considerably reducing manual effort. It supports multi-stage review workflows with consensus labeling, benchmark datasets, and automated quality checks.
Key Features:
- Native video timeline with playback controls
- Object tracking with scene switching
- Multi-stage review workflows and consensus labeling
- API/SDK for pipeline integration
- Catalog, Annotate, and Model Foundry products
Pros:
- Enterprise-ready with HIPAA and SOC 2 compliance
- Strong collaboration and project management
- Comprehensive quality control features
Cons:
- Higher cost for dense frame labeling
- Enterprise features require a sales contact
- Free: 500 LBU/month
- Starter: $0.10/LBU (decreases with volume)
- Enterprise: Custom pricing, volume discounts
Best For: Organizations requiring compliance (HIPAA, SOC 2), and projects needing model-assisted workflows with flexible consumption-based pricing.
Kili Technology
Kili Technology is a data labeling platform focused on helping teams build high-quality datasets with collaboration, quality-first workflows, and secure deployment options. It supports bounding boxes and classification with intuitive playback controls for videos.
Kili adds workflow helpers like adjustable propagation settings (to control how labels extend across frames), flexible controls to expand and contract the span of annotated frames, and “smart tracking” when you edit an annotation across frames.
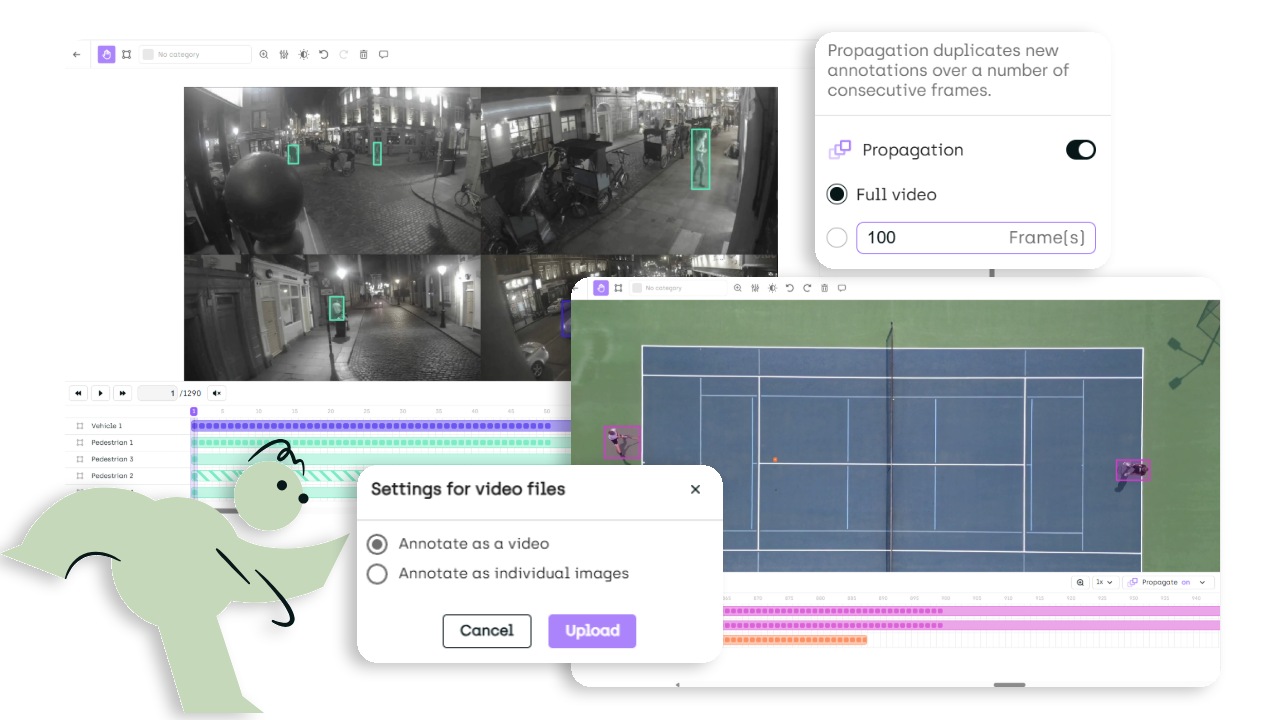
Key Features:
- Video Timeline with playback controls
- Smart tracking + keyframe interpolation
- Propagation tools
- Long video support (100K+ frames)
- Collaboration with activity logging
Pros:
- Modern timeline built for production video workflows
- Strong automation reduces repetitive frame labeling
- Quality-focused with clear audit trails
- Free trial for easy evaluation
Cons:
- Best automation requires consistent keyframing practices
- Paid plans sized for production-scale volumes
- Free Trial: 2 seats, 200 assets, basic features
- Grow: Up to 20 seats, 50K assets, API/SDK
- Enterprise: Custom pricing, professional services
Best For: ML teams that need a collaboration-first labeling platform with a tooling to speed up long-video annotation, and quality-focused workflows that scale across annotators and reviewers.
How To Choose The Best Video Annotation Tool
Selecting the right video annotation tool depends on your specific project requirements, team structure, and technical constraints.
Use the following decision framework to narrow your options.
- Start with Your Primary Use Case: If you need native video support with temporal context preservation (autonomous vehicles, surveillance, medical imaging), prioritize tools like Encord, Labelbox, and V7. For frame-by-frame analysis, frame-based tools like Unitlab AI, Roboflow, and CVAT work well.
- Team Expertise: Open-source annotation platforms like CVAT and Label Studio offer customization but require MLOps support. Commercial managed services, Unitlab AI, Labelbox, Encord, and Scale AI, provide out-of-the-box infrastructure and support.
- Volume and Budget: Free tiers suit small projects (<10k frames). Mid-sized (10k-100k) benefit from consumption-based models (Labelbox, Roboflow). Large enterprises (>100k) should evaluate Unitlab AI, Scale AI, or Encord for volume discounts or for a monthly subscription.
- Automation: For predictable object motion, choose platforms with AI assistance Encord and Unitlab AI). For custom models, API-first tools are best: Unitlab, V7, Roboflow, and CVAT.
- Quality Control: Enterprise projects need multi-stage review and automated QA, features offered by Unitlab AI, Labelbox, Encord, SuperAnnotate, and Scale AI. Smaller teams can use manual review (CVAT, Label Studio).
- Compliance and Security: Regulated industries (Healthcare, Finance) require compliance (HIPAA, SOC 2, GDPR) to be provided by commercial tools like Unitlab AI, Encord, Labelbox, and Scale AI, with flexible deployment. Self-hosted open-source tools require independent compliance management.
- Test Before Committing: Run a small pilot (100-500 frames) using free tiers on platforms like Unitlab AI, Labelbox, SuperAnnotate, CVAT, and Roboflow to evaluate speed, QA, and user experience before committing to a full rollout.
Key Takeaways
Video annotation transforms raw footage into structured training data and helps build vision models for real-world applications.
Video annotation captures temporal information, such as tracking objects across frames, maintaining persistent IDs, and understanding motion and context.
The best video annotation tools combine native video support, AI-assisted labeling, and robust quality control to accelerate workflows while maintaining accuracy.
Choosing the right video annotation tool depends on your specific requirements. Native video support for temporal context, AI-assisted automation for speed, compliance certifications for regulated industries, or API-first architectures for ML pipeline integration.
Most platforms offer free tiers or trials, so use these to pilot your workflow before committing to enterprise contracts.




