Unlike general 2D image annotation, medical annotation volumetric imaging, specialized formats such as DICOM and NIfTI, and and extremely high precision requirements.
A single CT or MRI study can contain hundreds to thousands of slices. These slices form a complete 3D representation of internal anatomy. Every slice may require precise segmentation, often at pixel-level accuracy, to train reliable clinical AI models.
Medical annotation tools must handle:
- Large volumetric datasets
- High-resolution imaging
- Complex segmentation workflows
- Multi-user collaboration and QA
- AI-assisted annotation pipelines
Without strong performance and proper tooling, medical annotation becomes slow, inconsistent, and difficult to scale.
Unitlab AI was built specifically to solve these challenges. Its architecture supports large multi-slice DICOM volumes, real-time 3D visualization, and AI-assisted segmentation workflows designed for clinical AI development.
This article explains the limitations of traditional medical annotation tools and how Unitlab enables scalable, high-performance medical annotation.
If you need a refresher on what medical annotation is and how it differs from traditional 2D RGB image labeling, check out our article on the topic:
Medical Image Annotation Guide
Limitations of Traditional Medical Annotation Tools
Many existing medical annotation tools were originally designed for visualization rather than dataset production. They work well for reviewing scans but struggle when used to create large annotated datasets for AI training.
These limitations become critical when working with modern clinical AI workflows.
Common limitations include:
- Slow DICOM rendering and poor performance with large studies
- No scalable annotation workflows
- Limited AI integration
Let's discuss these limitations.
Poor performance with large studies
Medical imaging datasets are large by nature.
A typical CT scan, called the study, can contain:
- 500 to 3,000 slices
- File sizes from 100 MB to over 1 GB
- High-resolution volumetric data (512x512 for CT to 2048x2048 for radiology to higher for specialized cases)
It is no wonder that many medical labeling tools, both current and non-current, experience slow loading times, UI lag when switching slices, UI instability with large annotation counts, and screen freezing during segmentation.
Needless to say, this slows down annotation workflows and reduces productivity. Instead of focusing on annotation quality, medical annotators spend time waiting for the interface to respond.
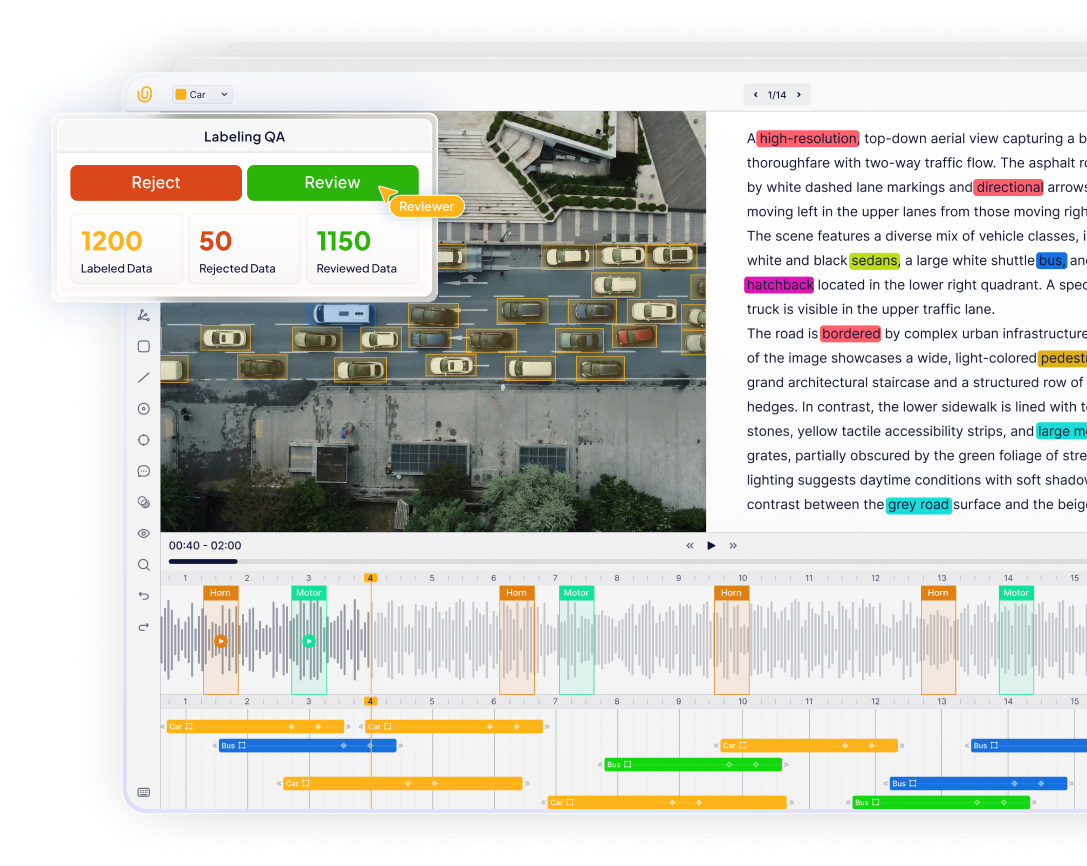
Limited support for collaboration and QA
A relic of the past, Most traditional tools were designed for individual radiologist use, not large-scale annotation teams. Medical dataset creation often requires close collaboration between data annotators, reviewers, doctors, and ML engineers. Without proper infrastructure, annotation quality decreases and production slows.
When annotating 1 hour of medical video can take more than 800 hours, you want your annotations to be as accurate as possible in the first try.
Most medical annotation platforms lack essential features such as structured annotation workflows, multi-stage review pipelines, annotation version control, dataset management and scaling tools.
This inadequate support for collaboration and QA in medical annotation workflows creates annotation quality, performance, and collaboration problems, slowing down dataset creation and curation for medical AI.
Weak AI integration
Modern annotation workflows rely on AI assistance. Instead of manually annotating every slice, AI models generate initial segmentation masks. Humans review and refine these results. This human-in-the-loop approach improves both speed and quality.
However, many traditional medical annotation tools do not integrate modern segmentation models such as SAM-based architectures. This forces annotators to perform repetitive manual segmentation, which is obviously very time-consuming and resource-intensive. This significantly increases annotation time and cost.
Comparison with Traditional Medical Annotation Tools
Most existing medical annotation tools focus primarily on visualization rather than scalable annotation. Unitlab addresses these limitations directly.
Here is a summary table which we will discuss in detail below:
| Capability | Traditional Tools | Unitlab AI |
|---|---|---|
| Large DICOM volume performance | Slow or unstable | Fast and stable |
| 3D annotation support | Limited or visualization only | Native annotation-ready 3D viewer |
| AI-assisted segmentation | Limited or unavailable | Integrated SAM3 and EfficientSAM |
| Annotation scalability | Limited | Production-scale support |
| Performance with large annotation counts | UI lag or freezing | Stable with 10,000+ annotations |
| Clinical dataset production | Not optimized | Built for AI dataset creation |
Why Unitlab AI Is Built for Clinical AI Teams
Enter Unitlab AI, a fully-automated data platform that combines performance, scalability, and AI assistance in one place.
It combines high-performance DICOM rendering, native 3D annotation, and integrated AI-assisted labeling workflows.
Let's see these benefits in more detail.
High-Performance DICOM Annotation and Rendering with Unitlab
First of all, Unitlab solves the technical challenge of DICOM rendering by optimizing both the frontend and backend piece of the visualizer extensively. That's it.
Our platform enables instant rendering and smooth scrolling even with large volumetric studies.
Fast DICOM rendering and slice navigation
Because of our focus on performance, speed, and user experience (annotator experience, to be precise), we focus firsthand on fast DICOM rendering and smooth slice navigation. We understand that working at an unstable work station and excessive waiting are frustrating for everyone.
That's why fast DICOM rendering was our top priority when we started working on our medical annotation tool. After a lot of testing and optimization, Unitlab AI now provides smooth slice scrolling, fast zooming and panning, and instant loading of large volumes.
This improves productivity and annotator experience significantly. The last thing you want while labeling complex medical slices is a slow, unresponsive, instable tool. So, with Unitlab AI, radiologists and data annotators can focus on clinical interpretation instead of waiting for the tool.
Fast DICOM SLice Rendering | Unitlab AI
Reliable handling of large medical datasets
Now that we solved the base performance problem of DICOM rendering, we focused on scaling. A typical CT study can have anywhere from tens to thousands of slices, so the problem was maintaining stable performance even at scale.
It was a difficult, yet fun engineering challenge: while most other tools have difficulty with one slice rendering, we managed to maintain stable performance even when handling long MRI sequences, high-resolution CT scans, large study volumes, and 10,000+ annotations per study.
The annotation interface remains responsive, enabling clinical annotation at production scale.
Native 3D Medical Annotation and Visualization
It is one thing to render DICOM/NIfTI files fast for visualization, and it is quite another to provide an intuitive, comfortable, and useful work station for medical annotators. Once the rendering and performance parts were handled, we focused on essential aspects needed for effective clinical labeling.
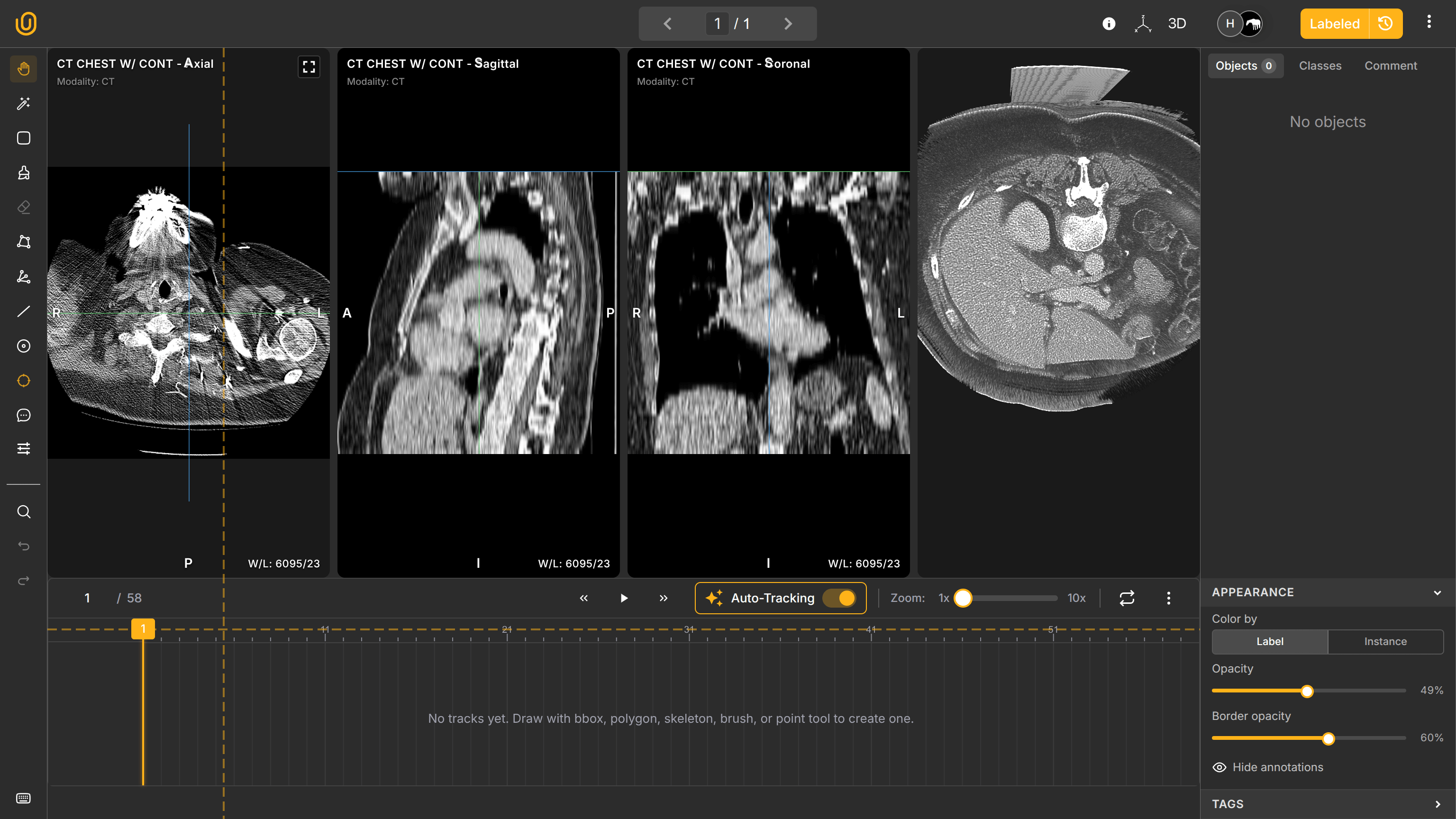
Medical imaging is inherently three-dimensional. Understanding anatomical structures requires volumetric context views: Axial view (top-down), Sagittal view (side), and Coronal view (front). Combined, these make one 3D representation of an internal body and remain synchronized in real time.
Annotations created in one plane appear automatically across other planes. This ensures spatial consistency and improves annotation accuracy.
The annotation dashboard follows medical conventions: in slices, it shows A (Anterior - the front of the body), P (Posterior - the back of the body), R (Right - the right side), and L (Left - the left side). It also shows Hounsfield Units (HU) on the bottom left of the work station: Window Width (1460) for determining shades of gray and Window Length (-380) for determining brightness.
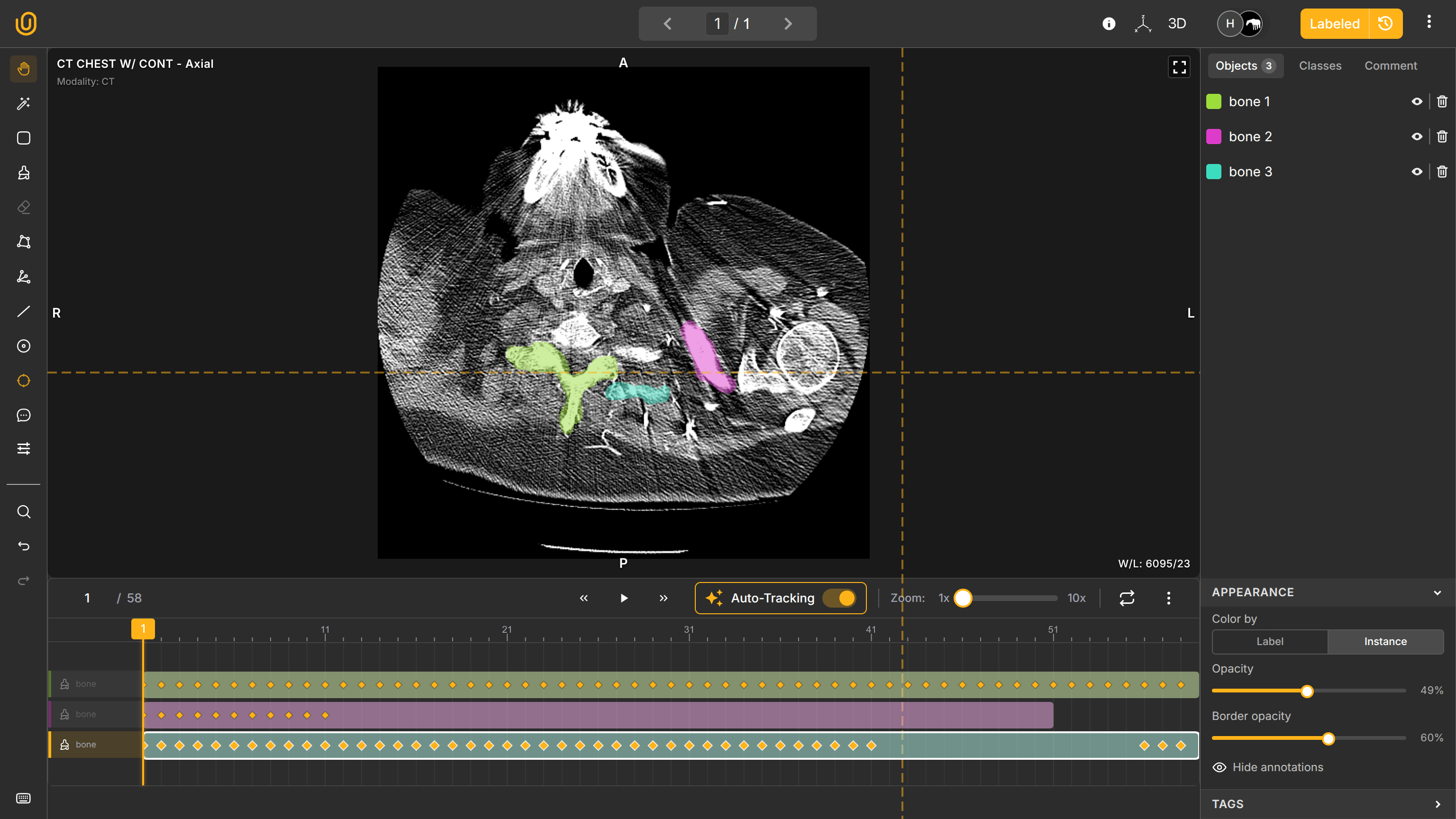
You can also activate the MPR view to see all fronts in one window: Axial, Sagittal, and Soronal. You annotate the Axial pane, and your annotations will automatically synchronize in other panes. Elegant, innit?
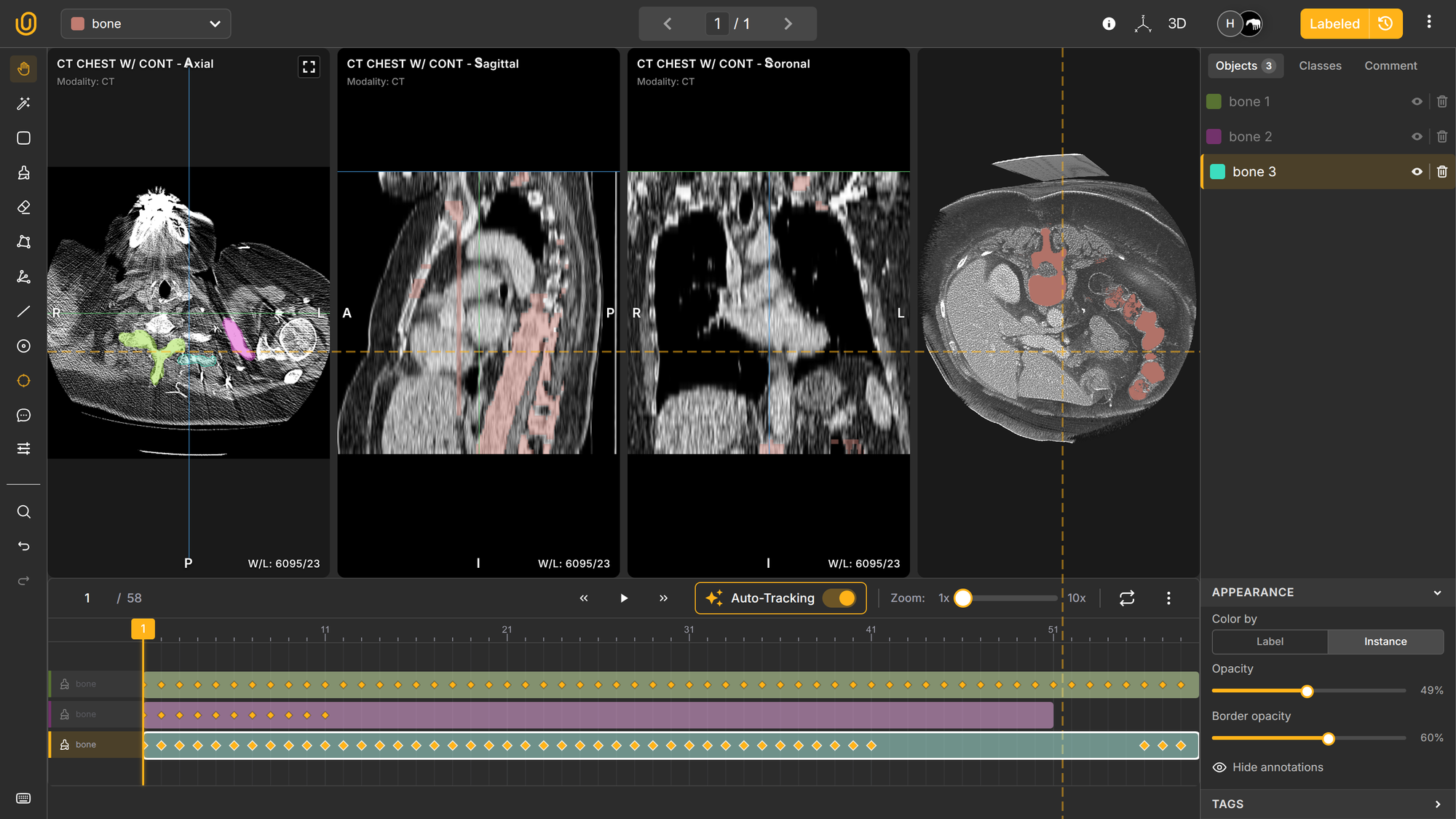
Additionally, you can interact with the actual 3D representation of the organ by enabling the 3D view on the top-right corner to observe how your annotations look like on the 3D plane:
3D Medical Annotation View | Unitlab AI
Finally, and this is the best part, you can configure standard medical conventions to make your DICOM file look exactly the way you want:
- Hounsfield Unit visualization
- Window level and width adjustments
- Color map configuration
- Customizable rendering parameters
Customizing Standard Medical Conventions
This provides a familiar and efficient environment for medical professionals.
So, we are offering a performant, scalable DICOM annotation tool that is customizable, intuitive, and follows medical conventions. Great, right? We have the last missing puzzle though: AI-assisted auto-annotation.
AI-Assisted Annotation with SAM-Based Models
The fact of life: AI-assisted auto-annotation, especially the human-in-the-loop approach, dramatically accelerates AI dataset creation while maintaining the baseline quality.
Facilitating thousands of data labeling projects at Unitlab AI, we know the value of modern AI-powered models for data annotation. That's why we provide modern segmentation models out of the box, such as SAM3 and EfficientSAM and provide a functionality to bring your own models (BYOM) to our platform.
Unitlab utilizes these SAM-based models to automate complex medical annotation tasks.
Automatic segmentation
Annotators can create segmentation masks automatically using integrated SAM-based models. This eliminates the need for manual pixel-by-pixel labeling. Human annotators focus on refinement rather than creation. This improves both speed and accuracy.
SAM-based auto-segmentation | Unitlab AI
Annotation propagation across slices
In medical imaging, structures in medical scans extend across multiple slices. With tens to thousands of CT scans in a single study, it is not the best approach to manually annotate each and every scan. With auto-tracking (interpolation), Unitlab automatically propagates segmentation across adjacent slices.
This ensures consistent annotation across volumetric datasets. Medical annotators no longer need to manually label every slice, reducing annotation time dramatically.
Instant Load Study
Performant, smooth slice navigation
Auto-segmentation based on SAM3
Auto-tracking (interpolation) across slices
Quick human refinement
Complete datasets faster
Enabling Real-World Clinical AI Applications
Unitlab supports dataset creation for a wide range of clinical AI systems. These include:
- Tumor detection and segmentation
- Organ segmentation
- Radiology workflow automation
- Disease progression monitoring
- Medical imaging research
High-quality annotation directly improves model accuracy and reliability. Unitlab enables medical AI teams to build these datasets efficiently.
Conclusion
Medical annotation requires specialized tools capable of handling volumetric imaging, large datasets, and precise segmentation workflows.
Traditional medical annotation tools were not designed for modern clinical AI development. They struggle with performance, scalability, and automation.
Unitlab solves these challenges with high-performance DICOM rendering, native 3D annotation capabilities, and integrated AI-assisted segmentation.
This enables healthcare organizations, research teams, and AI companies to build high-quality clinical datasets faster and more efficiently.