Domain-specific AI equipped with vision holds immense potential for transforming and automating workflows across numerous industries. It is becoming an essential tool for human operators, enabling them to achieve levels of efficiency and precision that neither machines nor humans can attain independently.
Domain-specific AI, also known as Narrow AI or Task-specific AI, refers to systems designed to perform a limited set of tasks with exceptional specialization and efficiency. Examples include voice assistants like Amazon Alexa, facial recognition software, and recommendation engines used by Netflix.
Narrow AI is distinct from the much-discussed AI Agents, which employ general-purpose AI capable of performing a variety of tasks akin to human intelligence and learning to adapt. This article explores how domain-specific AI integrated with computer vision is transforming logistics operations, making it an indispensable tool for human operators.
By the end of this post, you will gain insights into:
- The prospects of computer vision in logistics.
- Specific applications of computer vision in logistics.
- The importance of data annotation in training Narrow AI.
Introduction
Logistics is the backbone of modern economies, ensuring the seamless movement of goods from manufacturers to consumers. As global supply chains grow increasingly complex, leveraging advanced technologies becomes essential to maintaining efficiency, security, and cost-effectiveness.
Among these technologies, computer vision is emerging as a game-changer, revolutionizing logistics through automation and enhanced accuracy.
Computer Vision in Logistics
Logistics is a critical sector in modern economies, heavily relied upon by global supply chains. The industry was valued at approximately $3,794.4 billion in 2023, with an expected annual growth rate of 7.2% from 2024 to 2030.
Given its significance and complexity, the adoption of AI technologies has become widespread among startups, corporations, and ports to automate operations, accelerate workflows, and empower human operators with cutting-edge tools.
Since logistics inherently involves visual tasks, the integration of computer vision with domain-specific AI offers transformative potential. Inspired by this YouTube video and Bloomberg article, we delved into this subject. Notably, Tianjin, a pioneering seaport in China, has already taken significant strides in revolutionizing port logistics through automation:
Computer Vision Transforming Sea Ports in China
Applications of Computer Vision in Logistics
The applications of Narrow AI powered by computer vision are extensive and adaptable across industries with minor customizations specific to an industry. Below are four prominent use cases specific to logistics:
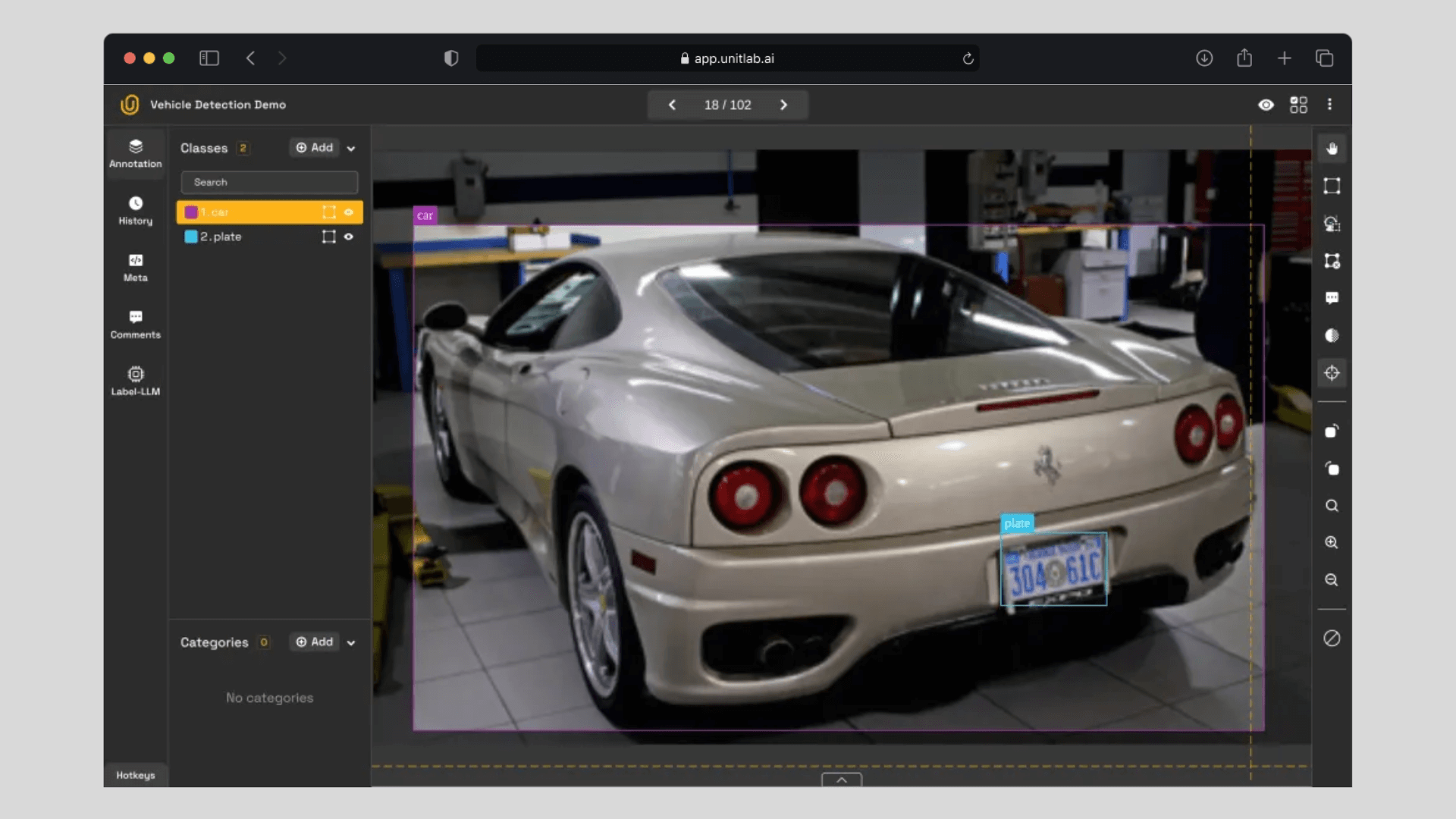
1. Vehicle Tracking and License Plate Recognition
One of the most straightforward applications is vehicle tracking and license plate recognition. Instead of relying on human operators to manually log entries, an AI model utilizing OCR can automatically record vehicles entering and exiting the premises. This technology can also be applied to ships.
This simple yet effective use case can automate numerous manual tasks. For instance, gates can grant access to authorized vehicles based on license plate recognition, directing them to assigned docks or distribution centers.
Applications:
- Fleet Management: Real-time tracking of delivery trucks.
- Access Control: Enhanced security by allowing only authorized vehicles.
- Dock Management: Automated vehicle assignment to specific destinations.
Impact:
- Streamlines operations by automating manual processes.
- Improves security with detailed logs of vehicle movements.
2. Warehouse Automation
Inventory management is a universal challenge, relevant across industries. Warehouses and distribution centers can leverage computer vision with specialized AI to enhance operations.
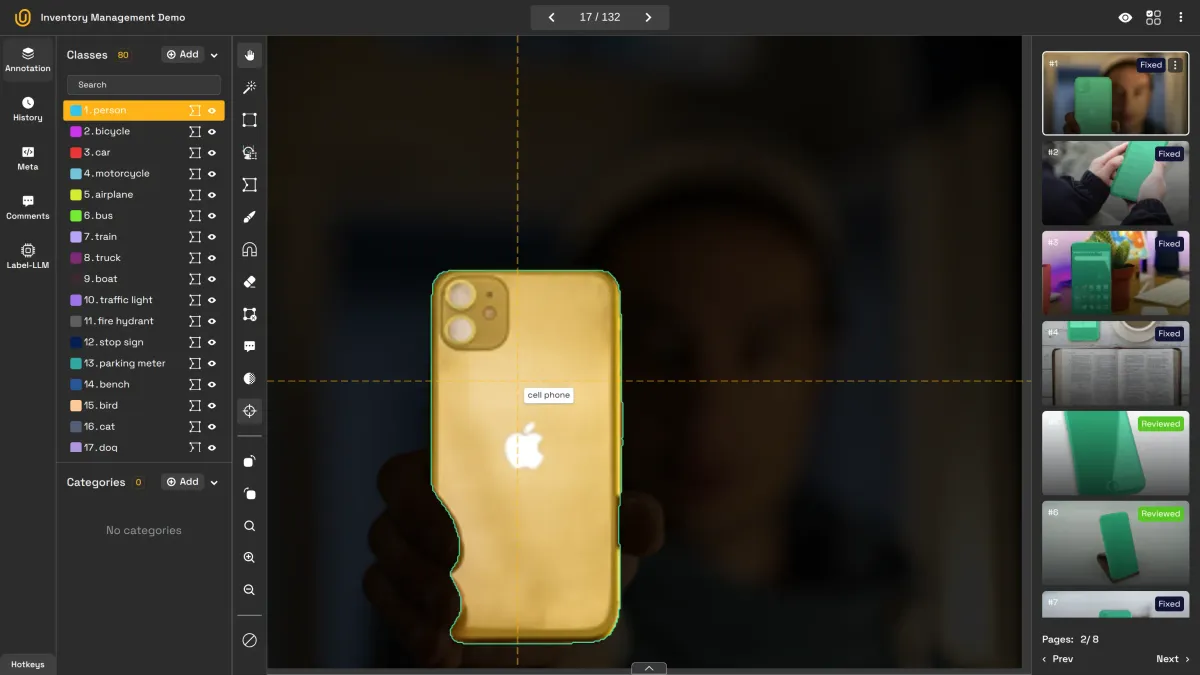
Enhancing Inventory Management with Computer Vision | Unitlab Annotate
Tasks such as detecting and classifying goods, or assigning items to containers, can be automated. This allows human operators to focus on assure quality rather than repetitive manual tasks.
Examples:
- Scanning and identifying packages on conveyor belts.
- Monitoring storage areas for overstocked or empty shelves.
- Guiding autonomous robots for item picking and transportation.
Benefits:
- Empowers human operators in inventory management.
- Accelerates order fulfillment processes.
3. Quality Control and Damage Detection
Traditionally, many manufacturers rely on acceptance sampling, where a random sample of items is inspected to estimate the quality of the entire batch. While effective for averages, this method does not pinpoint specific defective items, especially when conducted manually.
Computer vision AI can automate quality checks, inspecting goods in real-time and marking defective items for further review. This ensures a higher percentage of goods undergo quality assurance quickly and efficiently.
Features:
- High-resolution cameras detect dents, tears, or other signs of damage.
- Systems compare goods against standard specifications to ensure quality.
Outcome:
- Identifies damaged goods with precision.
- Enhances customer trust through consistent quality control.
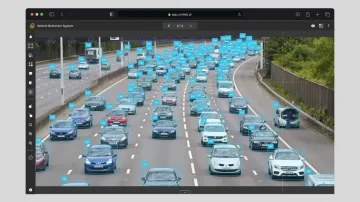
4. Route Optimization and Traffic Analysis
By analyzing data such as arrival and departure times, vehicle destinations, and license plates, domain-specific AI can optimize routes in real-time using Vehicle Routing Problem Algorithm and its variants. Historical data allows human analysts to detect congestion patterns and refine models for better accuracy.
Capabilities:
- Collecting and analyzing data from roadside cameras.
- Identifying bottlenecks and suggesting alternative routes.
Advantages:
- Reduces fuel consumption and delivery times.
- Enhances safety by mitigating traffic congestion.
Importance of Quality Data Annotation in Logistics
While the potential of Narrow AI is immense, its success depends on meticulous training and deployment, which require significant investment of time and resources. Although the ROI (Return on Investment) is generally high, as demonstrated by the Tianjin port case, careful attention is essential to avoid developing subpar AI models, which we call humorously Garbage AI , that fail to meet expectations.
Visual data annotation is the crucial foundation of computer vision model development. It is impossible to fix a model built on faulty data. High-quality, diverse annotated datasets yield better AI models. As you feed more and more data, the quality of AI models becomes higher over time.
Therefore, you need a way to manage different dataset versions of different projects. Managing dataset versions and leveraging data annotation tools, such as AI-powered auto-annotation, can streamline this process. At Unitlab AI, we emphasize workflows where human annotators correct mistakes and review outputs for consistency and accuracy.
Solution:
Choose a data annotation platform tailored to your project’s needs. Look for features like dataset management, model integration, and auto-annotation tools to optimize the annotation pipeline.
Batch Auto-Annotation | Unitlab Annotate
At Unitlab Annotate, we have developed a public dataset for vehicle and license plate recognition, available for free exploration, downloads, and cloning. Additionally, our platform supports auto-labeling tools and data annotation services to streamline workflows.
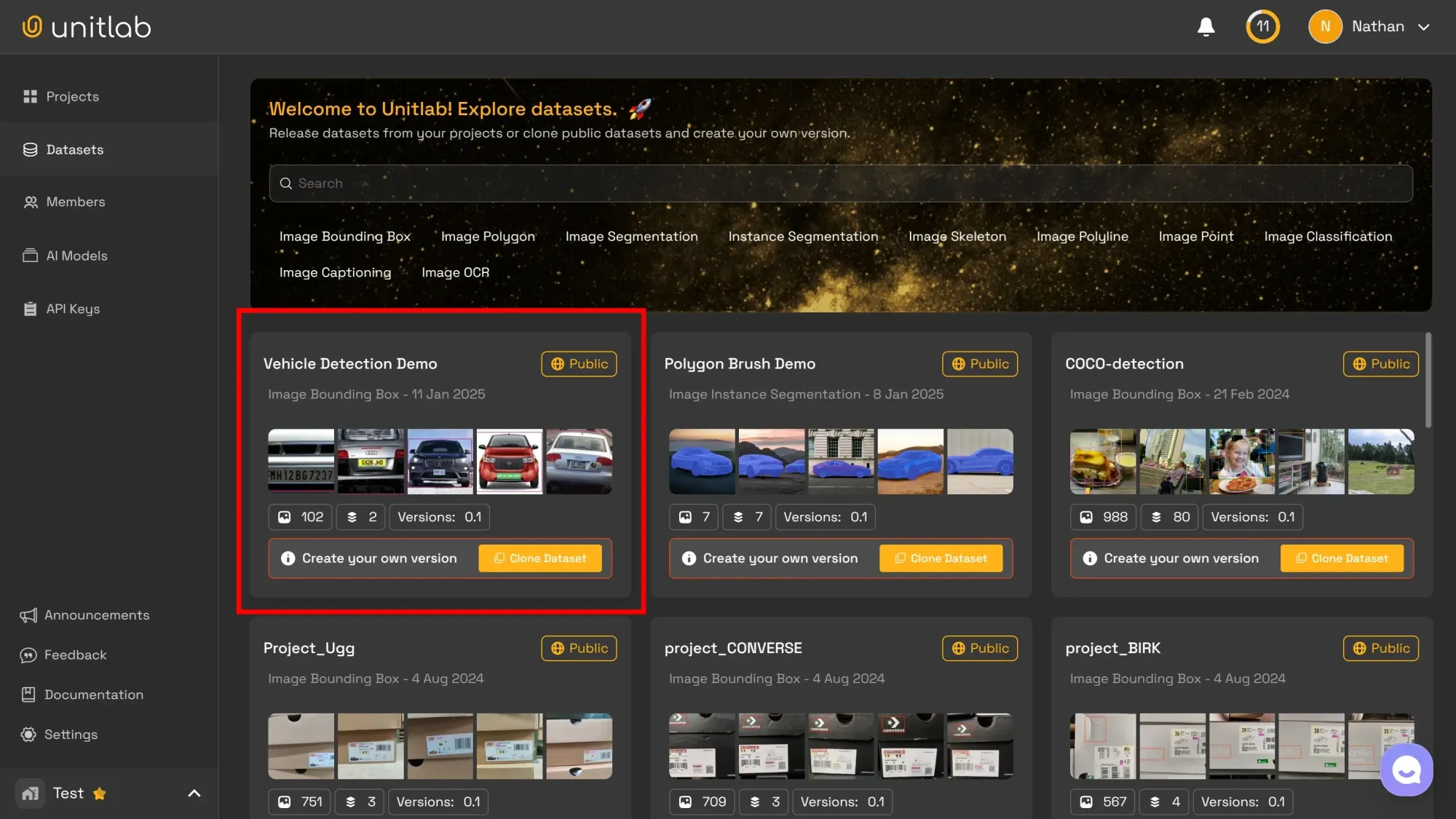
Conclusion
Computer vision is revolutionizing industries, including logistics and large sea ports. Its applications range from general to highly specific, enabling automation and empowering human operators in numerous industries and daily operations.
To achieve such efficiencies, developing high-quality AI models using annotated, industry-specific datasets is imperative. Leveraging the right image annotation solutions and dataset management tools is key to ensuring consistent results. Since data annotation presents its own challenges, selecting the right vendor is critical.
Image Annotation Tools Comparison | Unitlab Annotate
We have compiled a comprehensive overview of popular vendors in 2024. However, we strongly recommend extensive testing of platforms before making a commitment.
References
- Unitlab Blog
- Lumenalta. What are the different types of AI?
- Forbes. From Healthcare To Space: Top 10 Transformative Computer Vision Trends In 2024
- IBM. What are AI agents?
- Grand View Research. Logistics Market Size & Trends
- You Tube. The World’s Smartest Port: How China Won the Shipping Race
- Bloomberg. Major China Port Banks on Robots to Beat Post-Covid Disruptions
- Viso.ai. 25+ Applications of Computer Vision in Logistics (2024)
- Wikipedia. Acceptance sampling
- SynControl. 6 Traditional Quality Inspection Process Fails (& Software Solutions)
- Wikipedia. Vehicle routing problem
- Cogito Tech. Importance of Quality Data Annotation in Logistics
- Unitlab Docs
- Unitlab AI