When building multimodal AI models, choosing the right architecture matters. But the multimodal data annotation platforms you use to create cross-modal training data matter just as much.
Many multimodal models fail in production because the training data never captured real-world combinations of images, audio, text, and sensor inputs.
You need a multimodal ML annotation tool that works across different data types in parallel and ensures labels match these types, and automates tedious work with AI-assisted workflows.
Otherwise, your team ends up duct-taping single-modality tools and spreadsheets just to keep examples aligned.
Here’s what we cover in this guide:
- What multimodal data annotation is and why it matters?
- Multimodal data annotation vs. multi-type data annotation
- Factors to consider when selecting a multimodal annotation platform
- Top multimodal data annotation platforms and comparison matrix
- Challenges with multimodal data annotation
- Why leading AI teams choose Unitlab over other multimodal data annotation platforms
What Is Multimodal Data Annotation And Why Does It Matter?
Multimodal data annotation involves labeling and linking information from different sensory sources to create a unified, semantically rich ground truth dataset.
It includes types like RGB video, audio waveforms, text prompts, LiDAR point clouds, radar signals, and thermal imagery.
Single-modal annotation, which identifies patterns within a single data type (drawing a bounding box around a car in an image).
And multimodal annotation focuses on the synchronization and semantic relationships between data types.
Furthermore, multimodal data annotation tools helps develop AI architectures like multimodal large language models that can process and understand information from multiple input modalities.
For example, training a model for a robot to pick up a red apple when the alarm sounds. And for that, we require a dataset where the visual cue (red apple), the sound (alarm ringing), and the timing of the robot's gripper movement are all annotated and connected on the same timeline.
If the annotation tool fails to keep that alignment, the AI might make errors, such as missing the right moment to act, which could lead to operational failures.
Multimodal Data Annotation Vs. Multi-Type Data Annotation: Key Difference
Many of us think multimodal data annotation platforms are the same as the platforms that support multi-type data. But they differ in database architecture and user interface design.
Multi-type data annotation labels multiple separate data types. These data types coexist on the platform but are not necessarily connected within a single example.
For instance, a platform that lets users transcribe audio, draw bounding boxes on an unrelated image, and classify a separate text document.
On the other hand, multimodal annotation requires understanding how different data types relate to each other within the same instance.
For example, a car labeled in an image from a camera must match the segmented points of the same car in a LiDAR point cloud, even if the car is partly hidden in the picture.
Here is the summary table:
Factors to Consider When Selecting a Multimodal Annotation Platform
Choosing the right platform goes beyond brand names and feature lists. So, evaluate platforms on criteria that match your project's specific needs.
The wrong choice can cost your team months of delays and thousands in wasted annotation effort.
Here are several key capabilities that a good multimodal annotation platforms share:
- Multi-Modality Support: The most important thing is to confirm that the platform natively supports the needed data types. Many platforms say they support multiple modes, but they may have separate editors for audio and video that do not allow viewing both on the same timeline or label them side by side.
- Recommendation: If the project involves Image + Text (captioning), then ensure the multimodal CV annotation platform allows parallel viewing and linking of text to specific image regions. If Audio is involved, verify that a waveform visualizer is time-synced with other visual inputs.
- AI-Assisted Labeling: Manual multimodal labeling is slow, so a tool with AI-assisted features can considerably speed up the labeling process.
- Recommendation: Look for Model-in-the-loop features. Does the platform allow you to plug in your own preliminary models to pre-label data? Does it offer interactive tools that assist manual annotators in real-time? Tools that offer active learning (selecting the most confusing samples for human review) can reduce labeling volume considerably.
- Data Management and Integration: A strong tool offers dataset versioning, standard exports, and APIs and SDKs so annotated data flows easily into your ML pipeline. For vision-language or voice-AI projects, check that it can export paired image–text or audio–text records in the right format.
- Recommendation: Check for a Python SDK and API support (offered by Unitlab). Programmatically uploading data, triggering annotation jobs, and downloading labels are essential for integrating the tool into a CI/CD pipeline (MLOps).
- Collaboration and Security: Since multimodal projects often involve large teams, features like role-based access, task assignment, communication threads, and progress dashboards are essential. Enterprise-grade security (on-premise options, encryption, compliance) is also needed for sensitive data.
- Recommendation: If working in healthcare or EU markets, verify SOC 2 Type II, HIPAA, and GDPR compliance. On-premises solutions (offered by Unitlab) are often mandatory for defense or for highly sensitive financial data, where cloud storage is prohibited.
- Cross-Modal Quality Control: The platform should include workflow and review features that check alignment between modalities. Look for version control, review and approval stages, and cross-validation tools.
- Usability and Scalability: The interface should keep annotators productive even as datasets grow. Intuitive UIs, customizable annotation templates, and performance analytics all help teams label faster.
- Cost Model: Finally, consider pricing and licensing. Some platforms charge per project, per hour, or per annotation, and open-source tools may be free but offer less multimodal.
Top 8 Multimodal Data Annotation Platforms
Now let's review the top multimodal data annotation platforms, focusing on their features related to multimodal workflows.
Unitlab AI
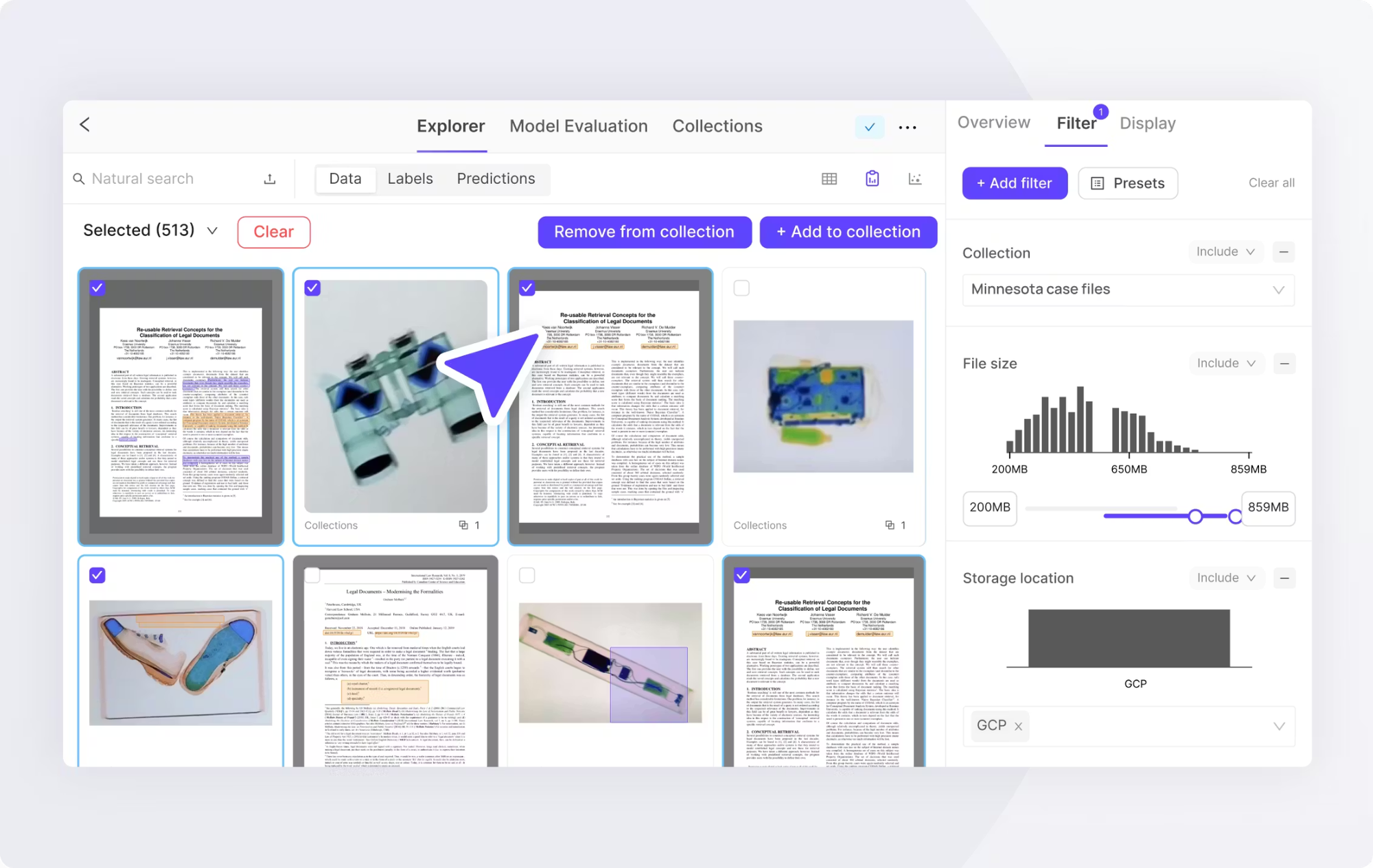
Figure 1: Unitlab multimodal data annotation.
Unitlab AI is a data annotation platform that supports images, video, text, audio, and medical data. And it is actively evolving toward full multimodal support. It focuses on synchronized, cross-modal labeling from the ground up as part of its roadmap.
Unitlab lets teams annotate different data types in a single workspace. Upcoming features will introduce native cross‑modal timelines and relationship graphs to make multimodal workflows first‑class.
Annotators work with all modalities side-by-side in a single view, making relationships explicit and easy to validate.
Furthermore, Unitlab supports secure, real-time collaboration. Teams get role-based access, versioned annotation history, and in-platform communication for feedback.
Key Features:
- Auto-Annotation Suite: Unitlab provides auto-annotating tools such as Magic Touch, Batch Auto-Annotation, and Crop Auto-Annotation. These tools use a foundation multi-model and SAM too, to automate labeling and speed up annotation by 15x compared to manual methods.
- Modality Support: The platform natively supports images, video, text, and audio, and integrates custom AI models (Bring Your Own (BYO)) to pre-label these data types.
- Collaborative Workspace: It features a project management environment with role-based access, real-time collaboration, and detailed performance analytics for tracking annotator efficiency and data quality.
- On-Premises and Hybrid Deployment: Enterprise and security-conscious companies can deploy Unitlab on-premises, keeping data within their secure infrastructure.

- Free: Unlimited workspaces, up to 3 members, and a limit of 5k to 10k source images or auto-labels.
- Active: $99 per month ($89 if annual), includes 5 members, 10k auto-labeling actions, and private datasets.
- Pro: $195 per month ($180 annual), supports 10 members and 25k auto-labeling actions.
- Enterprise: Custom pricing for unlimited members and source images, plus dedicated engineering support.
Best for: Unitlab is great for AI teams building autonomous systems, multimodal LLMs, robotics platforms, and healthcare AI systems where cross-modal consistency is non-negotiable. Also valuable for organizations that need to scale annotation across multiple teams and require strong quality control and compliance features.
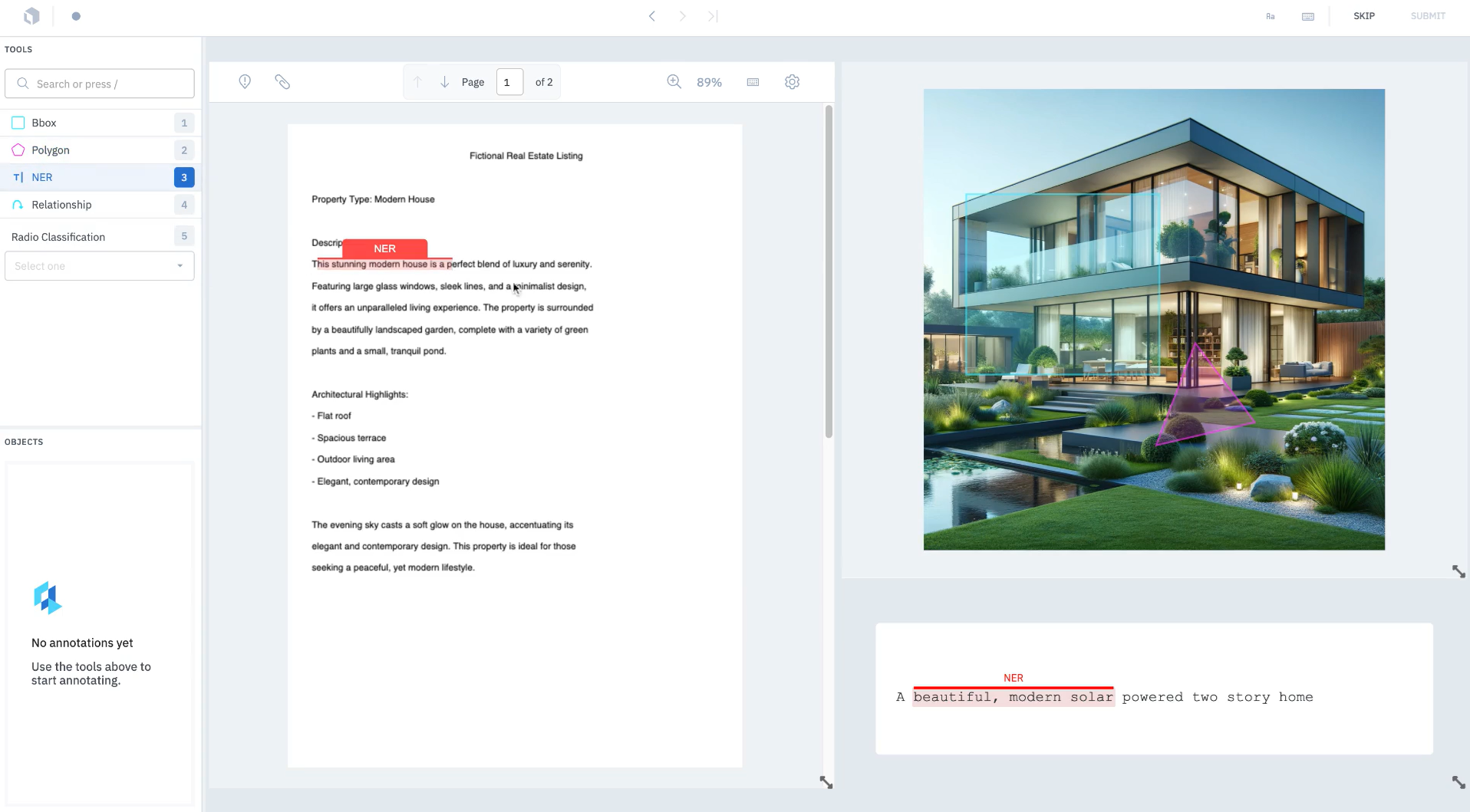
Encord
Encord is another multimodal annotation tool, particularly for computer vision and video data, combined with metadata and text. It provides video annotation with frame-by-frame precision and supports adding structured data, captions, and external information to video tasks.
Key Features:
- Encord Index: A tool for curating and visualizing large-scale datasets before annotation, and helps teams select the most impactful data to label.
- Micro-Models: It lets users build micro-models on small subsets of data to automate the labeling of the rest of the dataset, a form of active learning that reduces manual effort.
- Native Multimodal Support: It supports modalities such as DICOM, video, audio, and documents, with features for linking them (syncing audio transcripts with video frames).
- Traceability: Encord provides full audit trails and data lineage tracking, which are crucial for regulated industries such as healthcare (HIPAA compliance) and finance.
- Starter: Free for small teams or individuals.
- Team: Subscription-based (pricing is not publicly available, but usage or seat-based).
- Enterprise: Custom pricing depending on data volume and features.
Best for: Enterprise AI teams in regulated sectors and those building complex multimodal applications requiring data curation and active learning loops.
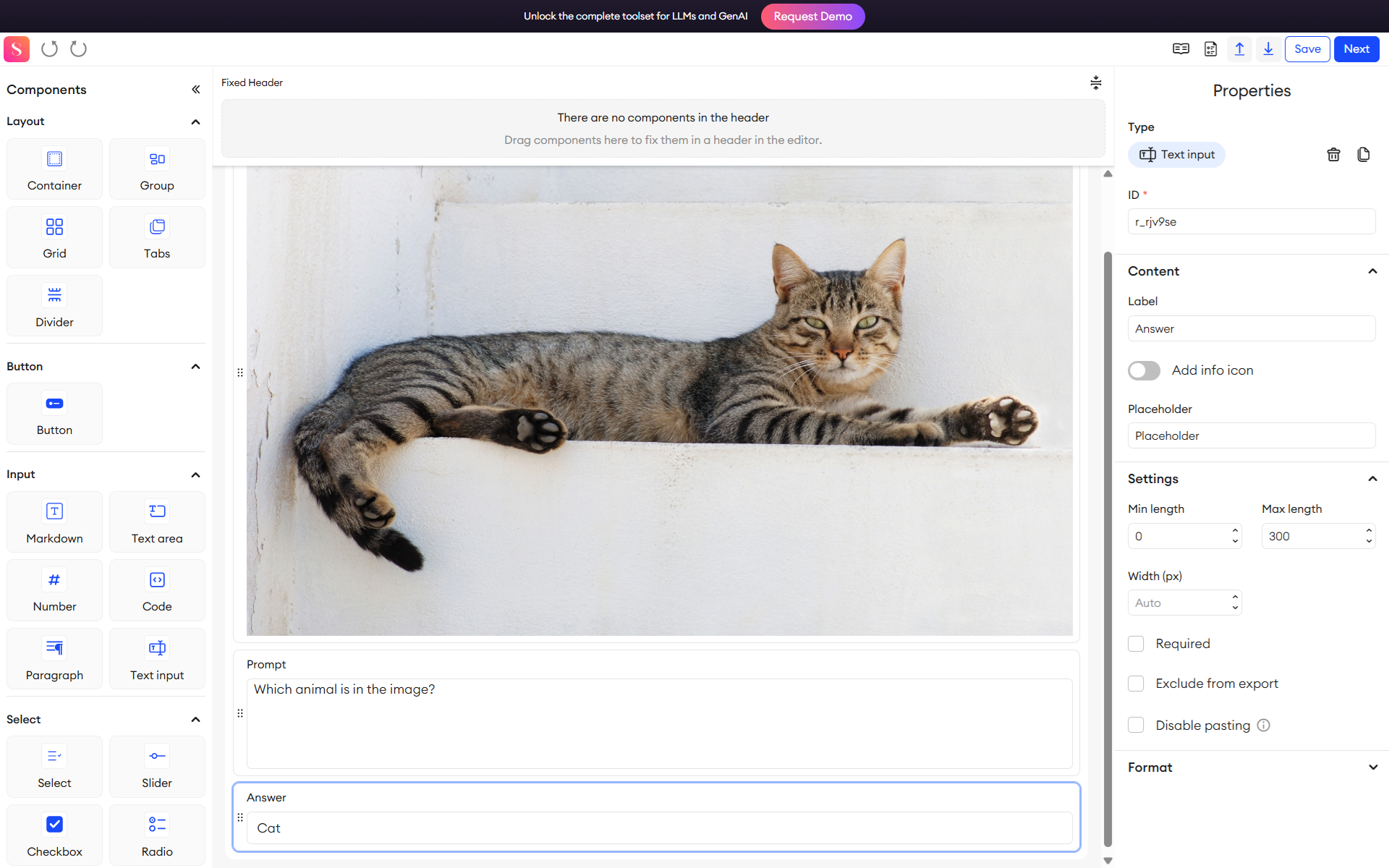
Labelbox's Label Blocks
Labelbox is a widely used tool to handle images, video, text, audio, GIS, and even HTML data.
It provides workflow automation, custom ontologies, data analytics dashboards, and model-assisted labeling.
Labelbox allows teams to set up project-specific workflows and uses a single metric for label quality.
Key Features:
- Label Blocks Interface: Labelbox customizable UI that allows teams to build annotation views by assembling different blocks (a video player block next to a text chat block), enabling bespoke multimodal workflows.
- Model-Assisted Labeling: It lets you import model predictions as pre-labels, which annotators then verify.
- Catalog and Discovery: Labelbox search and query engine for unstructured data to find specific data subsets, such as find all videos containing a red car at night, and then send for annotation.
- RLHF Support: It supports reinforcement learning from human feedback, especially for generative AI models involving text and image pairs.
- Free: Limited usage (500 Labeling Units - LBUs).
- Starter: Pay-as-you-go based on LBUs. Pricing depends on consumption and increases linearly with volume.
- Enterprise: Custom contracts with volume discounts.
Best for: Labelbox's Label Blocks are ideal for teams with complex, custom annotation workflows that require flexibility. Also, a good choice if you need to orchestrate annotation tasks across modalities without tight temporal synchronization.
SuperAnnotate
SuperAnnotate is a multimodal CV annotation platform that supports images, video, and 3D data, and text, too. It uses AI-assisted features, including automated object detection and segmentation, to speed up labeling with efficiency.
SuperAnnotate offers a visual interface for complex annotation tasks and includes quality assurance tools to monitor annotator performance.
Key Features:
- Multimodal Editor: A specialized interface for LLM and GenAI tasks, supporting RLHF, Supervised Fine-Tuning (SFT), and chatbot evaluation. It allows for the creation of complex forms with text, image, and video components.
- Integrated Management: Combines annotation, project management, and quality assurance in one platform. It supports "bring your own model" for automation.
- Hybrid Workforce: Offers both the software platform and access to a managed workforce of annotators, providing flexibility for scaling.
- Starter: Custom quotes.
- Pro: Includes advanced automation and project management.
- Enterprise: Volume-based pricing.
Best for: SuperAnnotate is ideal for teams focused on computer vision projects that integrate text, metadata, or 3D data.
Mindkosh
Mindkosh supports multiple data types, including images, documents, and text. It includes quality assurance tools, team collaboration features, and audit trails for compliance.
Mindkosh can be deployed on-premises for organizations with strict data residency requirements. But Mindkosh's multimodal capabilities are more basic compared to specialized platforms.
Key Features:
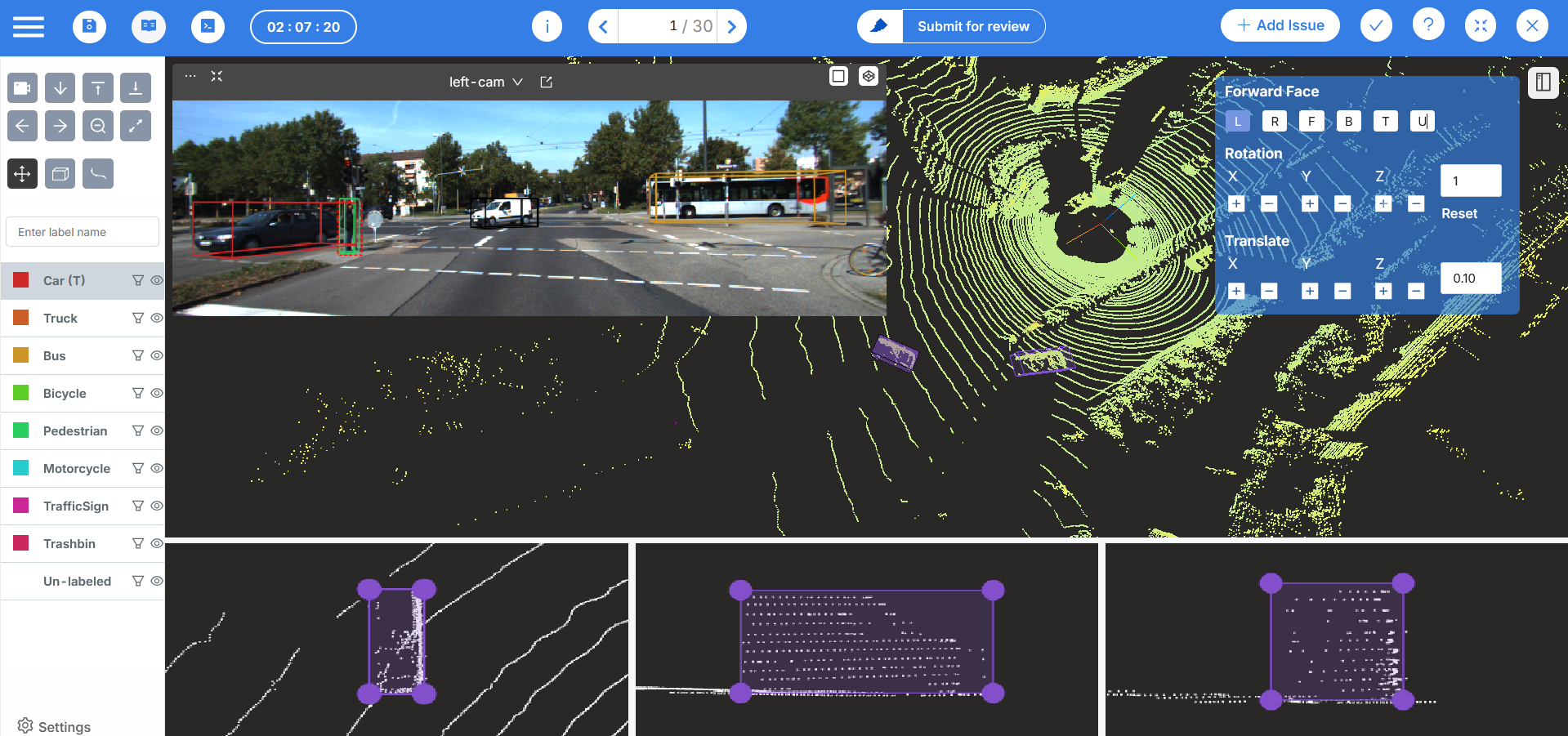
- Deep Sensor Fusion: Advanced tools for visualizing and labeling synchronized LiDAR, Radar, and Camera feeds. It supports one-click cuboid annotation in 3D space.
- Optimization: The platform is engineered to render massive point clouds (millions of points) smoothly in the browser.
- Automated Pre-labeling: It offers AI tools like Magic Segment and Mask Propagation across frames, plus 3D cuboid projection from LiDAR to images.
- Credit-Based System: A unique pricing model based on credits (annotation hours), offering flexibility for project-based work.
- Standard Image: Around $350 for 1000 credits.
- Standard LiDAR: Approximately $700 for 1000 credits (a $200/month subscription plus credits).
- Pay-as-you-go: Flexible credit purchasing.
Best for: Autonomous-driving and robotics teams focusing on multi-modal sensor data. Mindkosh is tailored to complex sensor fusion use cases where annotators benefit from seeing RGB+thermal/depth simultaneously and projecting 3D labels to 2D images.
Multimodal Data Annotation Platforms Comparison Matrix
The following matrix evaluates the above-mentioned multimodal ML annotation platform across key multimodal features. You can use it to quickly spot which tools match your needs for synchronization, automation, and collaboration.
Challenges Come with Multimodal Data Annotation?
Multimodal ML annotation is inherently more complex than single-modality labeling.
First, it’s more time-consuming and costly. Annotators may need to align hours of video with audio or transcripts, doubling the workload.
Ensuring consistency across modalities is another challenge. A feature that is obvious in one modality might be subtle in another (a spoken word in audio vs. a gesture in video).
Annotators also need specialized skills for each modality. So staffing becomes trickier as one must find personnel who can interpret LiDAR point clouds and understand nuanced audio sentiment.
Moreover, quality control must be stricter, as even a small mismatch (like a wrong caption on an image or a 50ms sync error) can greatly degrade model performance.
Key Takeaways
Multimodal data annotation helps build modern AI systems that can simultaneously understand multiple types of information.
When selecting a multimodal ML annotation platform, distinguish between true multimodal tools and multi-type platforms that handle multiple file types separately.
Look for native temporal synchronization, explicit cross-modal relationship support, strong AI-assisted features, and enterprise-grade quality assurance.
Evaluate platforms based on your specific modalities, workflow complexity, team size, and compliance requirements.
If you want a fast, high‑quality annotation solution, use Unitlab’s labeling services today!

![Best Multimodal ML Data Annotation Tools in 2026 [Comparative Guide]](/content/images/size/w2000/2025/12/Robotics--4-.png)

![The Ultimate Guide to Multimodal AI [Technical Explanation & Use Cases]](/content/images/size/w360/2025/12/Robotics--6-.png)