Developing Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML) models that accurately mimic human behavior depends heavily on training and testing, in turn, well-labeled datasets. The quality of an ML model cannot exceed that of its source data, a principle known as garbage in, garbage out.
To train computer vision models, models that can process, interpret, and predict using visual data, we need high-quality, well-labeled, consistent image sets. Image annotation, a subset of data annotation, involves tagging visual data to make it understandable to machines, enabling computer vision systems to interpret images.
Data Annotation: Types, Methods, Use Cases.
This post provides a detailed breakdown of the most common image annotation types, highlighting their purposes, methodologies, and real-world applications across various industries such as healthcare, autonomous driving, and retail.
We will use examples from Unitlab Annotate, a platform offering 100% automated and accurate data annotation, dataset curation, and model validation. Due to its focus on AI-powered auto-annotation and the human-in-the-loop approach to data labeling, it accelerates data annotation by 15x and minimize costs by 5x using advanced auto-annotation tools.
This platform supports all image annotation types and uses advanced auto-annotation features, such as the crop, magic touch, and batch, to automate image labeling process in a cost-effective way.
In this guide, we will discuss these image annotation types and provide further resources on them:
- Bounding Boxes
- Semantic Segmentation
- Instance Segmentation
- Classification
- Skeletons
- OCR
- Captioning
- Line Annotation
- Point Annotation
Let's dive in.
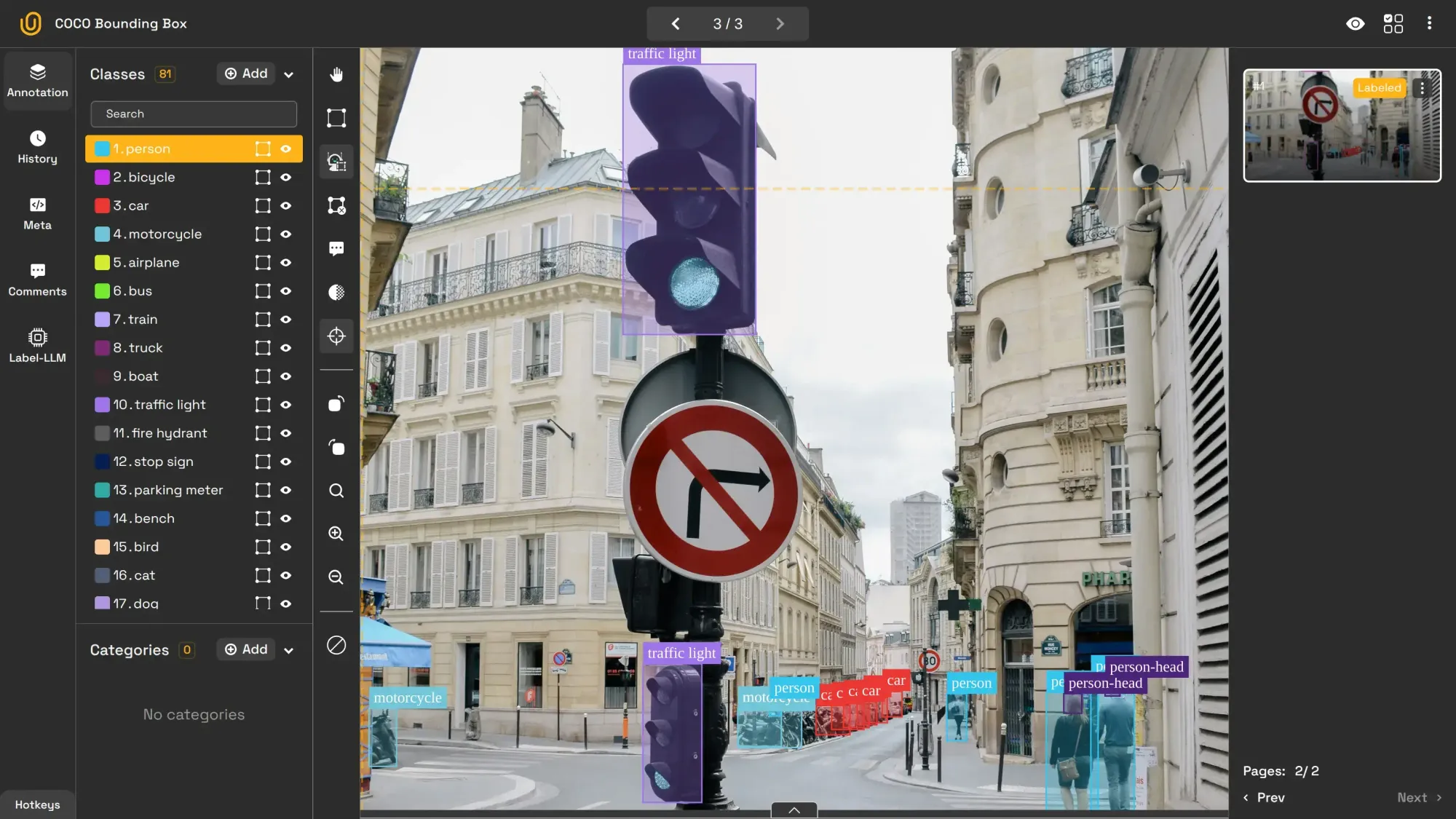
1. Image Bounding Box
A bounding box draws a rectangular frame around objects of interest to mark their location and size within the photo.
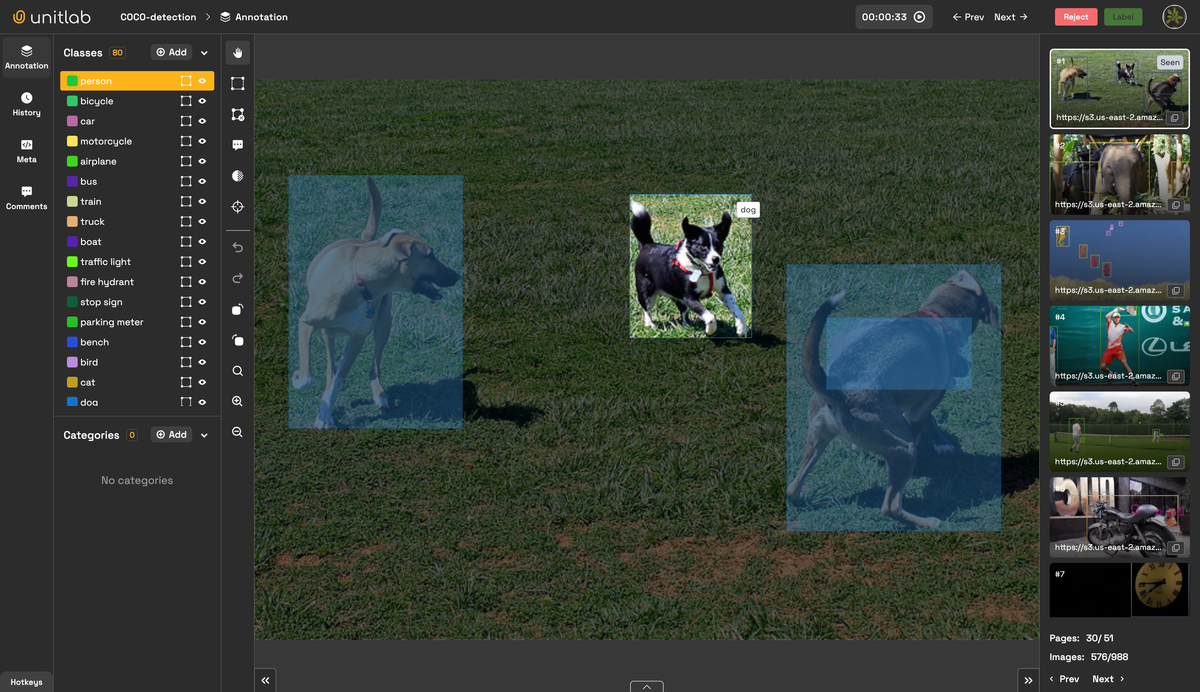
It is the most common image annotation type because it provides the simplest and easiest, though slightly inaccurate, method to train models to detect objects. For instance, the model can draw a bounding box around a cat to identify it in an image dataset. In the image below, an AI-powered auto-annotation tool draws rectangles around objects it idetifies.
This data annotation type is primarily used for these purposes:
- Autonomous Vehicles: Object detection (pedestrians, vehicles, road signs)
- Drones and Surveillance: Tracking objects or people in real-time
- Warehouse Management: Identifying and counting items on shelves
- Retail Analytics: Customer behavior tracking in stores
Because of its simplicity and popularity, it is usually the first entrypoint into image annotation:
Car Detection with Bounding Box | Unitlab Annotate
Check out this article for more on bounding boxes:
Bounding Box Essentials in Data Annotation
2. Image Segmentation
Image segmentation takes a more detailed approach by classifying every pixel in an image, assigning each pixel to a specific class, making it pixel-perfect.
Traditionally, most annotation methods work by outlining the coordination around the object of interest. Modern approaches, such as semantic segmentation, leverage pixels. In this type of segmentation, individual objects are not separated, but assigned a single class.
Because this type uses pixels, not coordinates to annotate, it provides a deeper understanding of scenes and objects for AI/ML objects. It can segment a street scene into roads, vehicles, pedestrians and buildings, for example.
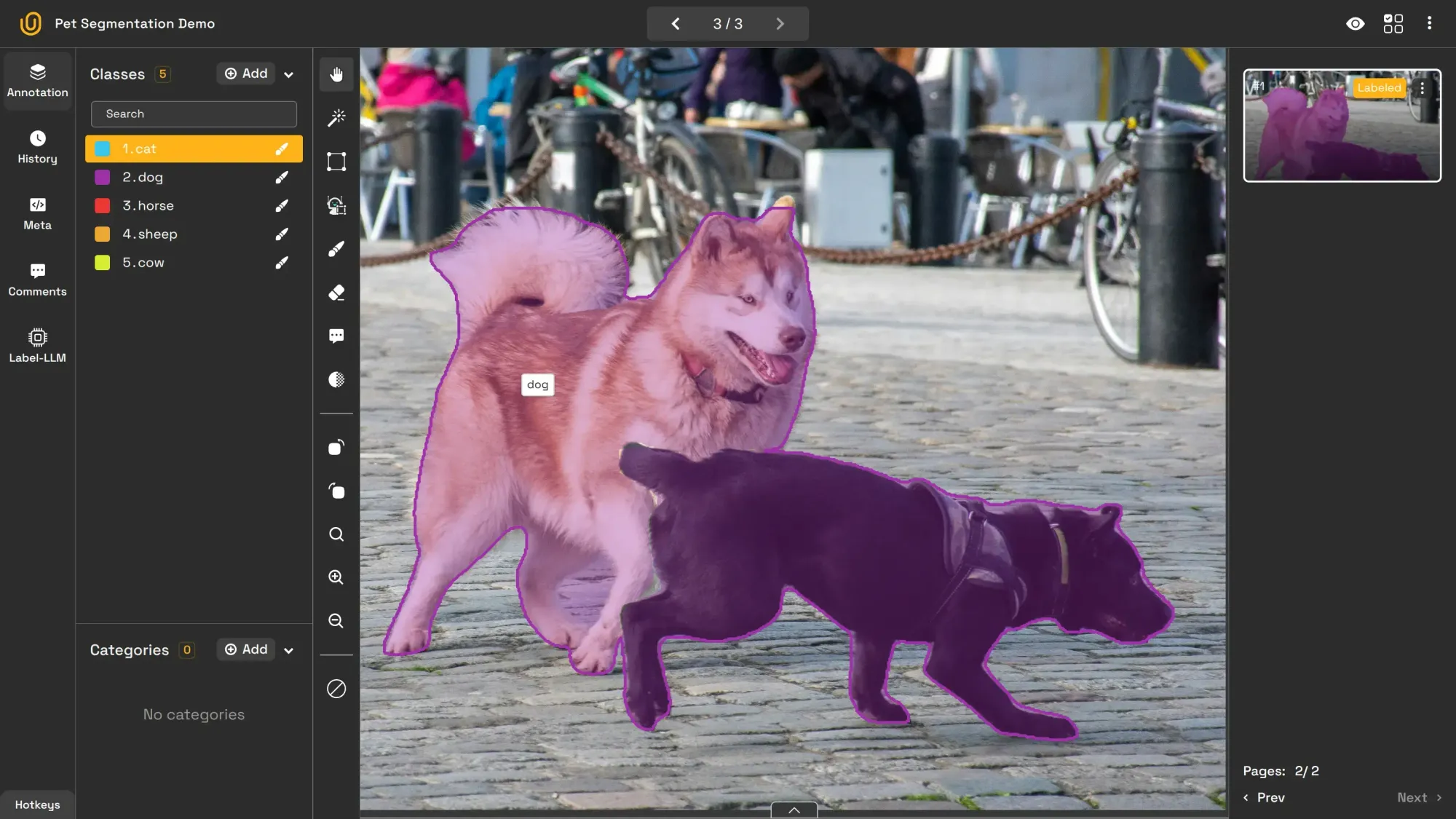

Its applications include:
- Self-Driving Cars: Lane detection, obstacle identification, and road segmentation
- Medical Imaging: Identifying tissues and abnormalities (e.g., tumor detection)
- Satellite Imagery: Mapping land-use and environmental features
Follow this tutorial to learn more about semantic segmentation:

Guide to Pixel Perfect Image Labeling
3. Image Instance Segmentation
Image instance segmentation not only segments objects but also distinguishes between multiple instances of the same category. For example, every apple in a basket is uniquely identified and segmented. Or, each car is uniquely identified, as shown in the image below.
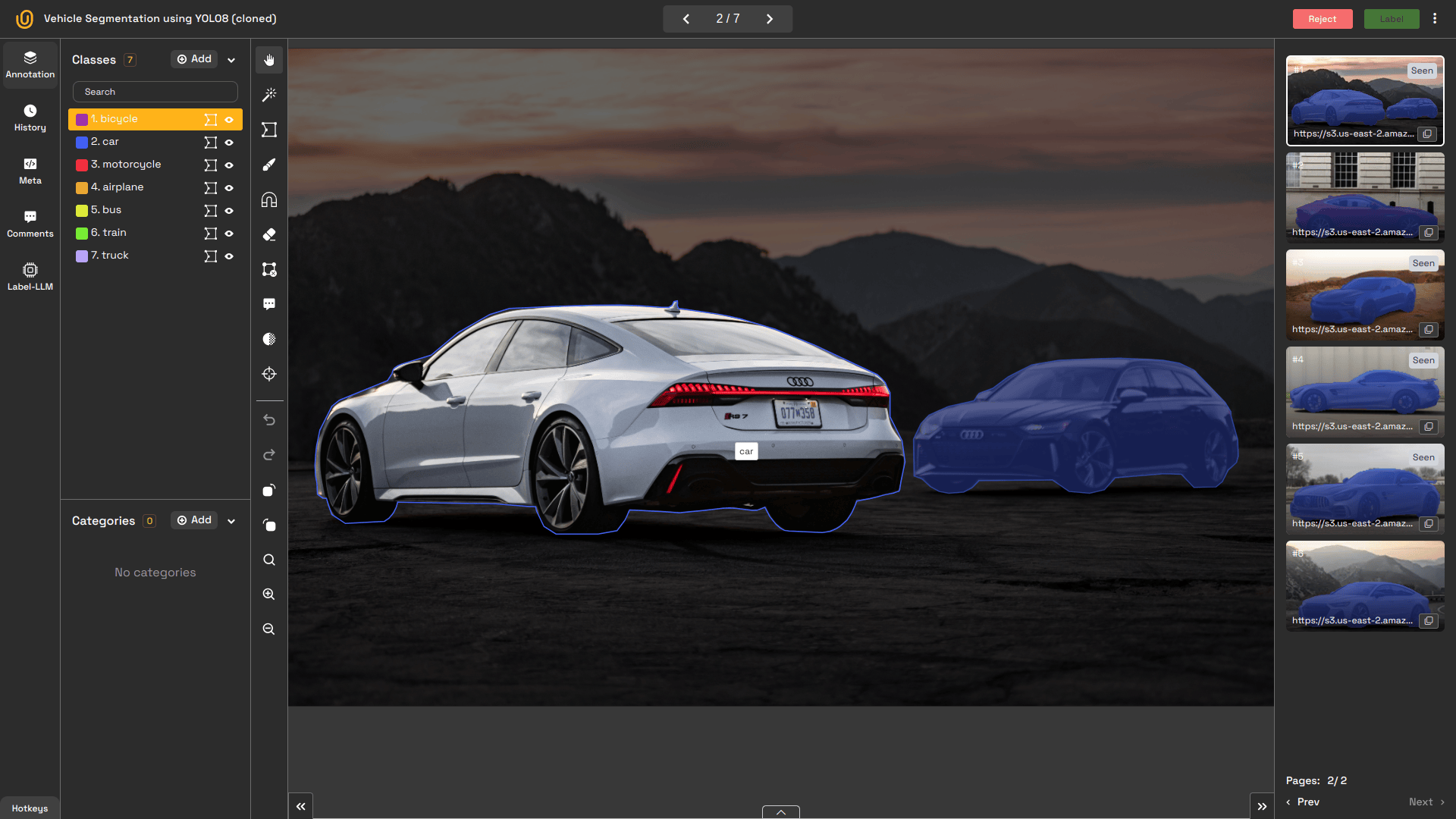
Also, this model can separate each person in a crowd scene or each car on a busy street. This type provides the exact location of each object in the image, as well as the count. The exact differences between semantic and instance segmentation can be found here:
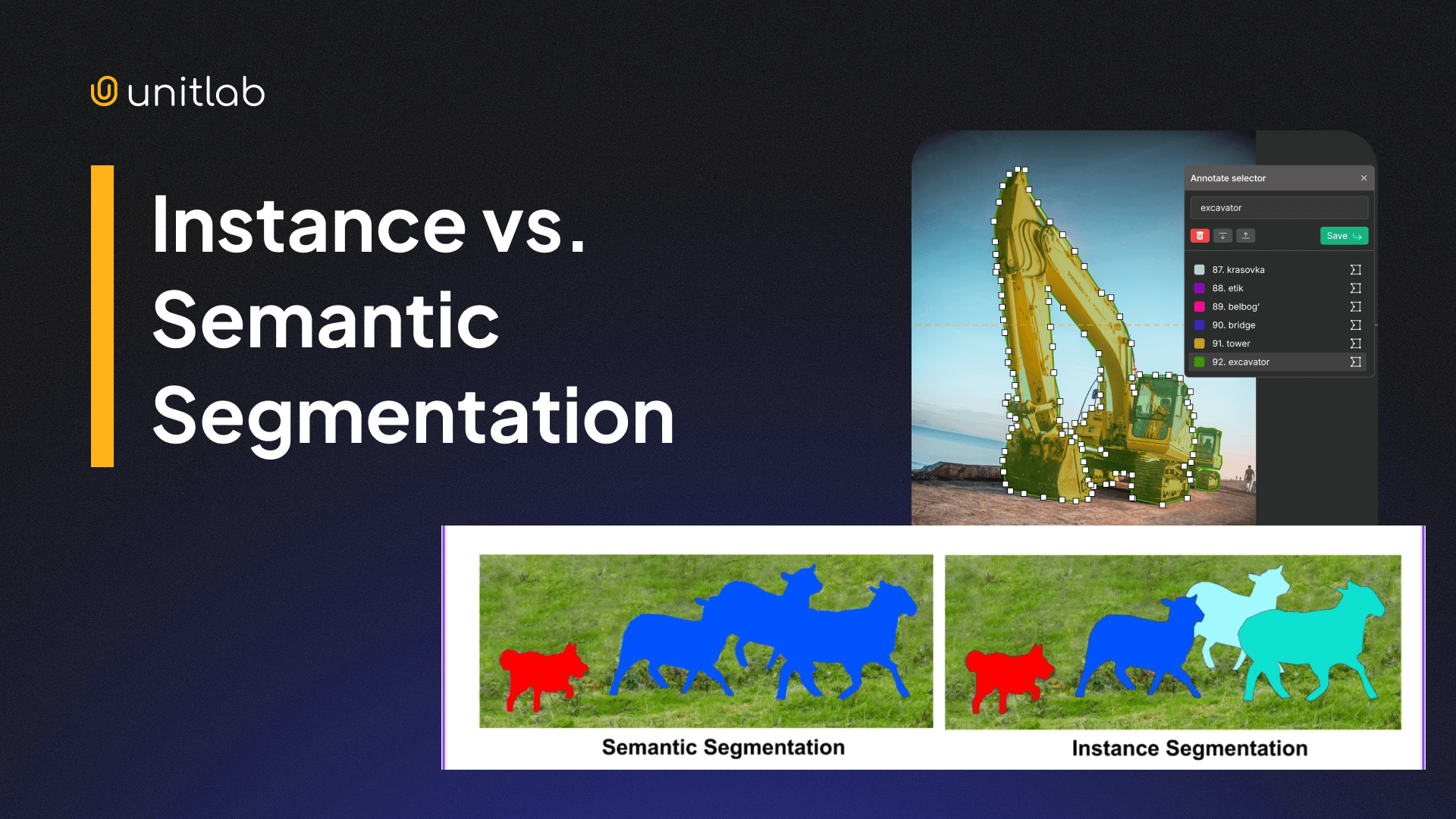
Semantic vs. Instance Segmentation: Key Differences
This model is particularly suited for:
- Healthcare: Identifying individual cells or lesions in microscopy images
- Autonomous Vehicles: Differentiating between multiple pedestrians
- Robotics: Assisting robotic arms in grasping distinct objects
This type of image annotation uses polygons, not pixels or boxes, to outline objects with irregular shapes to precisely capture their contours, which bounding boxes cannot do. This is particularly useful for objects with non-rectangular shapes. Satellites use this technique to outline the boundaries of buildings.

Read this tutorial to gain hands-on experience with instance segmentation:
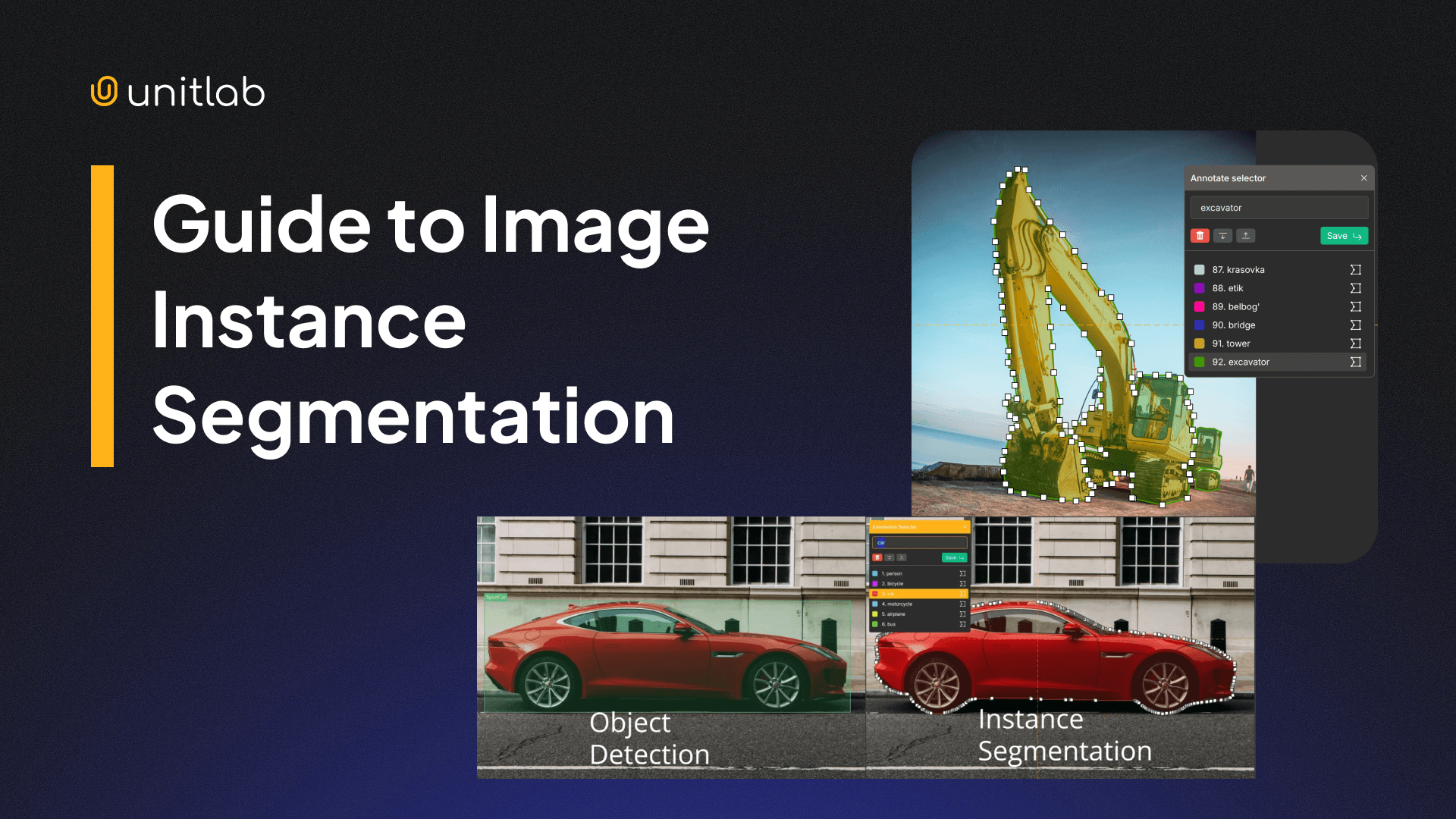
Instance Segmentation with a Demo Project
4. Image Classification
This type of model assigns labels to an entire image. Depending on the image’s content, it may have a single label (e.g., “dog” or “river”) or multiple labels (e.g., “dog,” “river,” and “forest”). An image classification model can even generate descriptive labels such as “a dog running alongside the river in the forest.” In this case, this becomes image captioning.

This type is primary used for assigning the label to the image:
- Search Engines: Categorizing images to improve search accuracy
- Social Media Platforms: Detecting inappropriate content automatically
- Healthcare: Classifying medical scans as healthy or abnormal
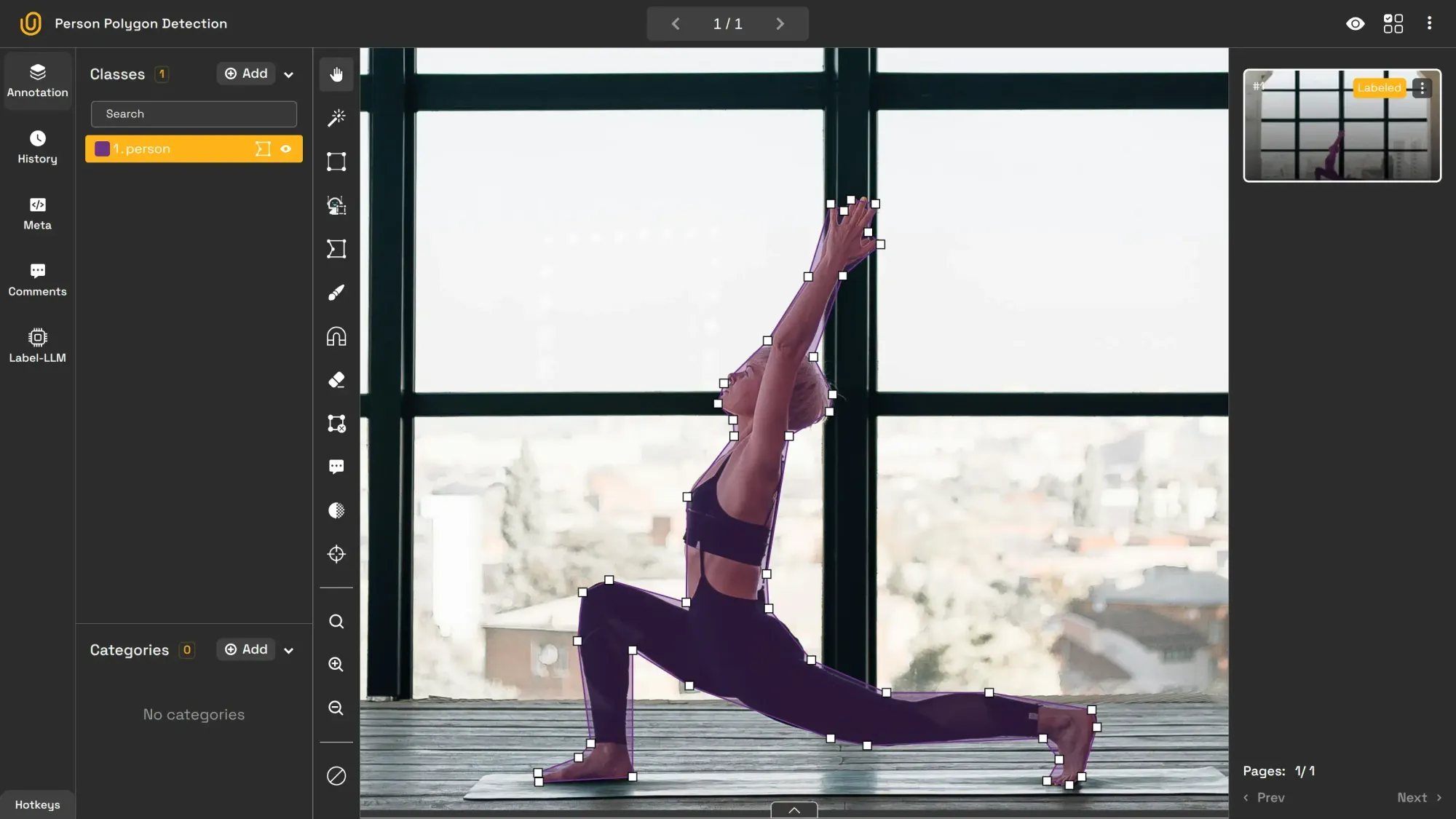
5. Image Skeleton Annotation
Image skeleton annotation maps an object’s structure by identifying key joints. It is often used in human pose estimation to track body parts such as shoulders, elbows, and knees. For instance, tracking a runner’s posture to analyze performance is one use case of skeletion annotation.
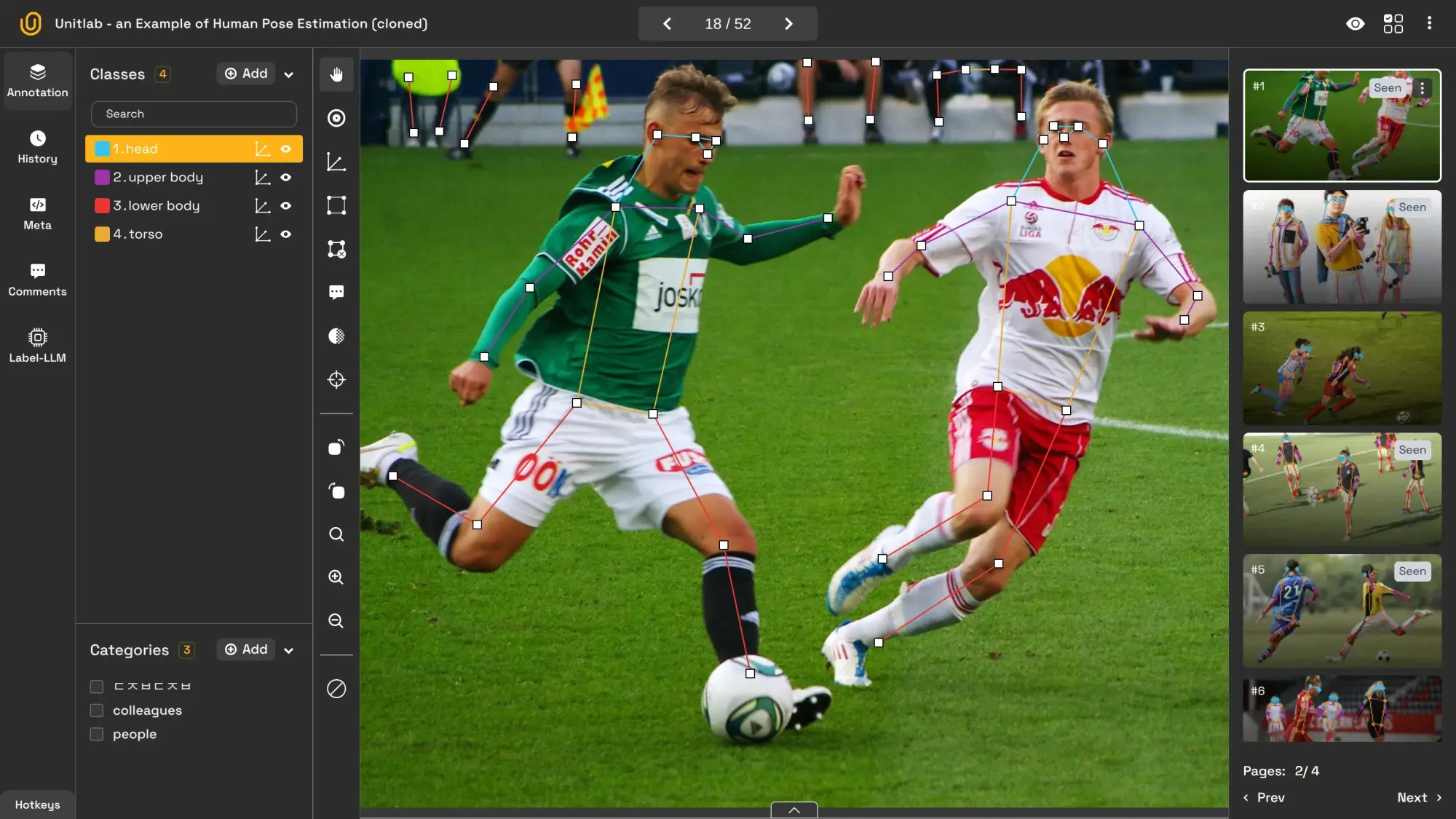
Its use cases include:
- Sports Analytics: Evaluating athletic movements and postures
- AR/VR and Gaming: Real-time body tracking for immersive experiences
- Driver Monitoring Systems: Detecting driver fatigue and drowsiness
Explore this article to get more in-depth information about image skeleton:

Guide to Effective Image Skeleton Annotation
6. Image OCR (Optical Character Recognition)
Image OCR extracts and digitizes text from images, making it machine-readable. It is extensively used for automating processes such as invoice management that involve written or printed text.
Scanners, speed cameras, and check processors heavily use this technology. Google Translate uses this technology to convert the image into text and then translates it into a chosen language.
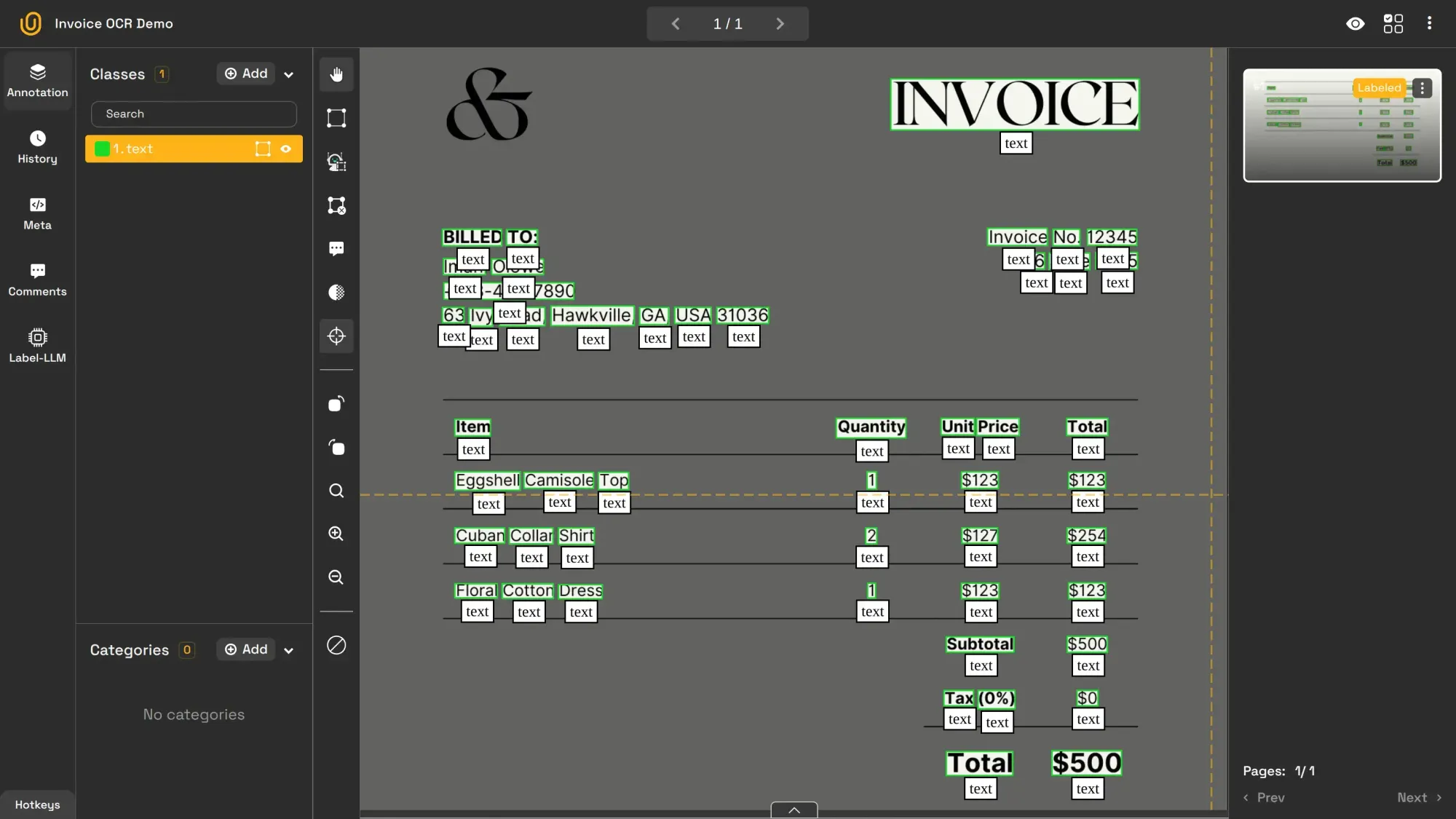
Image OCR is commonly used for these purposes:
- Traffic Management: Identifying vehicles through license plate recognition
- Banking: Automating check processing
- Document Management: Digitizing records and invoices
More comprehensive information on this topic can be found here:
Image OCR Annotation with Unitlab AI
7. Image Captioning
Image captioning, closely related to image classification, generates descriptive sentences that summarize the content of an image. It improves accessibility and enables better content organization and discovery. For example, when a user uploads an image to a social media website, the algorithm can automatically generate a tagline for the image for SEO purposes.
Image classification assigns a single label, for example cat, while captioning provides a descriptive info, such as A cat riding a skateboard.
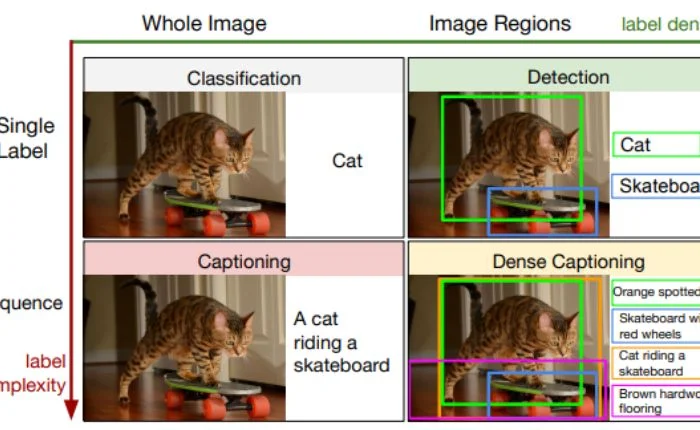
Image captioning is most helpful in these situations:
- Accessibility: Describing visual content for visually impaired users
- Social Media Platforms: Auto-generating captions for photos and videos
- Search Engines: Enhancing image search with accurate text descriptions
8. Image Line Annotation
Image line annotation is used to mark linear elements like roads, paths, or edges within an image. This image annotation type is essential for applications requiring structural mapping. For example, self-driving cars use image line annotation to detect lane boundaries on the road.
Thus, this model is primarily for line detection cases:
- Self-Driving Cars: Lane detection and path planning
- Cartography: Mapping roads and other infrastructure
- Architectural Design: Creating digital blueprints from scanned floor plans
9. Image Point Annotation
Finally, in image point annotation, specific points of interest are marked within an image. It is frequently used for facial recognition or medical diagnostics. For instance, it can mark the position of eyes, nose, and mouth in a face image.

Image point annotation is utilized in these situations:
- Facial Recognition: Identifying key facial features
- Medical Diagnostics: Pinpointing areas of concern in radiology scans
- Sports Analytics: Tracking player positions and ball movement in real time
Follow this tutorial for more on image point annotation:
Image Point Annotation
Conclusion
Image annotation is the foundation of computer vision models and applications. Whether enabling autonomous vehicles to detect road obstacles, helping doctors analyze medical images, or powering search engines with more accurate image recognition, each image annotation type serves a specific purpose.
Choosing the right type of annotation ensures the best performance for your computer vision project. By understanding these methods and their applications, data scientists and engineers can build robust AI systems capable of tackling real-world challenges.
Unitlab AI is ready to accelerate image annotation process by 15x with its advanced AI-powered auto-annotation models. This boost saves time and cuts cost by 5x.

![A Guide to Image Annotation Types [2026]](/content/images/size/w2000/2026/01/Image-Annotation.png)









