In our blog, we have extensively covered computer vision, its applications, challenges, and solutions. Recently, we discussed what computer vision fundamentally is and the top 5 open-source CV models that can be used to work with visual data. Now, to complete this discussion, we have taken the time to research the best computer vision courses for you to explore as you enter the fascinating realm of computer vision.
By the end of this post, you will learn:
- Factors to consider when choosing a computer vision course
- Top 5 computer vision courses available
Introduction
Computer vision essentially involves enabling machines to “see” the world and interpret visual data. It belongs to the broader AI field and is employed in many industries (often alongside AI) to conduct visual tasks and analyze visual data. Autonomous vehicles, robotics, and medical imaging are among the most common examples.
Since computer vision is part of AI, it operates at the frontiers of science, which means it evolves rapidly and receives considerable research attention from prestigious universities and technology corporations.
It is not limited to academia; in fact, the global computer vision market size is projected to grow by 27.3% annually, rising from $25.41 billion in 2024 to $175.72 billion in 2032. This is undoubtedly an exciting time to learn about computer vision.
This post is designed for anyone interested in learning computer vision. Regardless of whether you are a complete beginner from a different field, a software engineer, a statistician, or a data annotator, you will gain valuable insights because each course will be covered comprehensively.
Definition of 'Best'
As with all engineering fields, the definition of “best” is subjective. Choosing the right course depends on you and the course. Let us consider each set of factors separately:
'You' factors:
- Your Background: If you have a non-technical background, an introductory course in math, coding, and computer vision may serve you best. Conversely, if your background is in a technical domain (e.g., mathematics, physics, or engineering), you may prefer an intermediate course, with an emphasis on building real projects.
- Your Plans: What do you hope to achieve? Would you like to begin a career in computer vision or simply enhance your skills? For instance, a software engineer creating CV applications may have different objectives than an engineering student who aims to start a career in computer vision.
- Your Budget: Are you looking for free courses to gain familiarity, or are you prepared to purchase a comprehensive course to secure your first computer vision role?
'Course' factors:
- Curriculum Depth: How comprehensive is the course content? Does it address core CV fundamentals, intermediate topics, and more advanced themes?
- Practical Projects: Is it purely a lecture-oriented course offering topical overviews, or does it incorporate practical projects you can build and showcase?
- Flexibility: Can you proceed at your own pace, or does the course follow a fixed schedule?
- Community: Does the course offer a platform for asking questions, and is there instructor support if you need it?
While it is not possible to address every “you” factor here, we have conducted thorough research on “course” factors, so that you can make an informed decision based on your situation.
Top 5 CV Courses
These five CV courses are not ranked; they are designed for different audiences and needs.
Fast.ai’s Practical Deep Learning for Coders
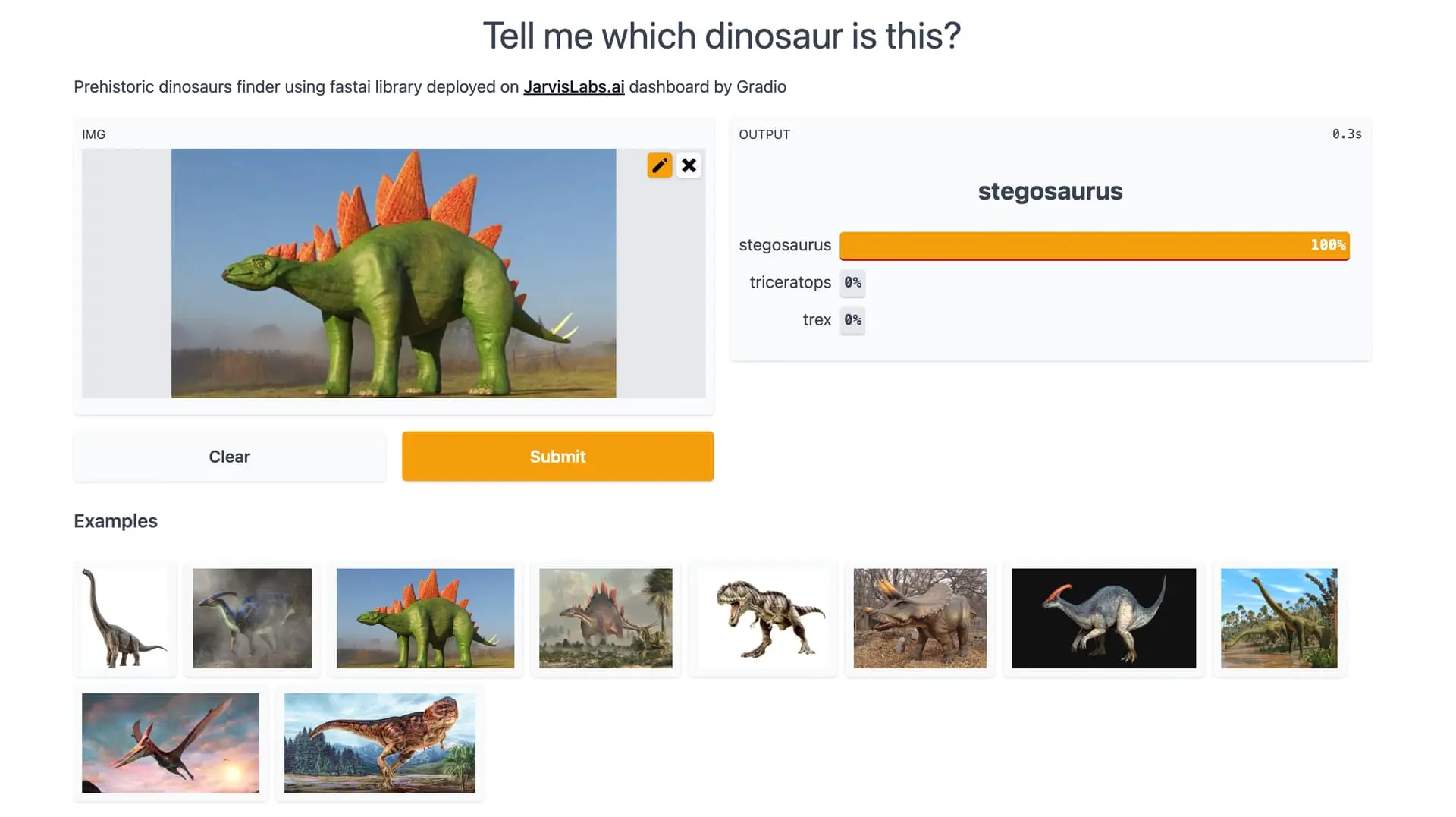
Short Description: A practical, project-focused deep learning course for participants with coding experience, offered by fast.ai.
Details:
- Platform: fast.ai
- Pricing: Free
- Level: Beginner to Intermediate
- Projects/Assignments: Yes
- Duration: Self-paced
If you have some coding experience (ideally in Python) and a solid understanding of high school math, this course may be the most valuable option for you. It is delivered by Jeremy Howard, co-founder of fast.ai, a non-profit AI research organization. It is a free, widely accessible course known for its emphasis on hands-on projects.
Although it is not solely dedicated to computer vision, it covers the use of deep learning in practical applications, including CV models. You will build, deploy, and fine-tune models, making it highly project-focused. Through its practical approach, you will also gain insights into preparing data, such as data annotation, to ensure your models have accurately labeled images.
Pros:
- Comprehensive Content: The course addresses practical deep learning fundamentals, with a more advanced second part.
- Free Access: Course materials, the book, and related software are all free.
- Project-centric: You will create working models applicable to real-world tasks.
- Community: A forum on the platform is available for discussions.
- Expert Instructors: Jeremy Howard brings extensive experience in both academia and industry.
Cons:
- Prerequisites: Requires a foundation in coding and mathematics.
Deep Learning for Computer Vision by University of Michigan
Short Description: A thorough theoretical overview of computer vision by the University of Michigan.
Details:
- Platform: YouTube
- Pricing: Free
- Level: Intermediate
- Projects/Assignments: No
- Duration: Self-paced
This course, provided by the University of Michigan and taught by Justin Johnson, is freely available on YouTube and includes supplementary slides and learning materials. It offers a theoretical overview of computer vision, covering topics from fundamental concepts to advanced deep learning techniques (generative models, reinforcement learning, and more). Being an academic course, it is highly structured and organized.
Pros:
- Comprehensive Content: Covers a broad scope of computer vision topics and delivers an excellent theoretical foundation.
- Free Access: Both the course and its supplementary materials are freely accessible.
- Expert Instructors: Taught by Justin Johnson, PhD, ensuring high-quality instruction.
Cons:
- Outdated Content: Although most content remains relevant, it was recorded in 2019, and many developments have occurred since then.
- Lack of Assignments: As a free theoretical course on YouTube, it does not include formal assignments or practical projects.
- No Community: There is no forum or direct instructor support.
Introduction to Computer Vision and Image Processing by IBM
Short Description: IBM’s beginner-level introduction to computer vision, delivered via Coursera.
Details:
- Platform: Coursera
- Pricing: Paid
- Level: Beginner
- Projects/Assignments: Yes
- Duration: Self-paced
This course from IBM, hosted on Coursera, is the most beginner-friendly course on this list. It is an ideal entry point for those who want to explore computer vision, providing both theoretical and practical perspectives and making use of IBM’s platform. It addresses various topics, ranging from image processing to machine learning classification, and culminates with a final project.
Pros:
- Beginner-Friendly: Concentrates on fundamental concepts and practical applications, avoiding overly complex material.
- Assigment-centric: Each module features assignments and projects, with free access to IBM’s platform.
- Community: Coursera offers discussion forums and instructor support.
Cons:
- Pricing: The cost may be prohibitive, but Coursera does provide financial aid.
Stanford’s CS231n: Deep Learning for Computer Vision
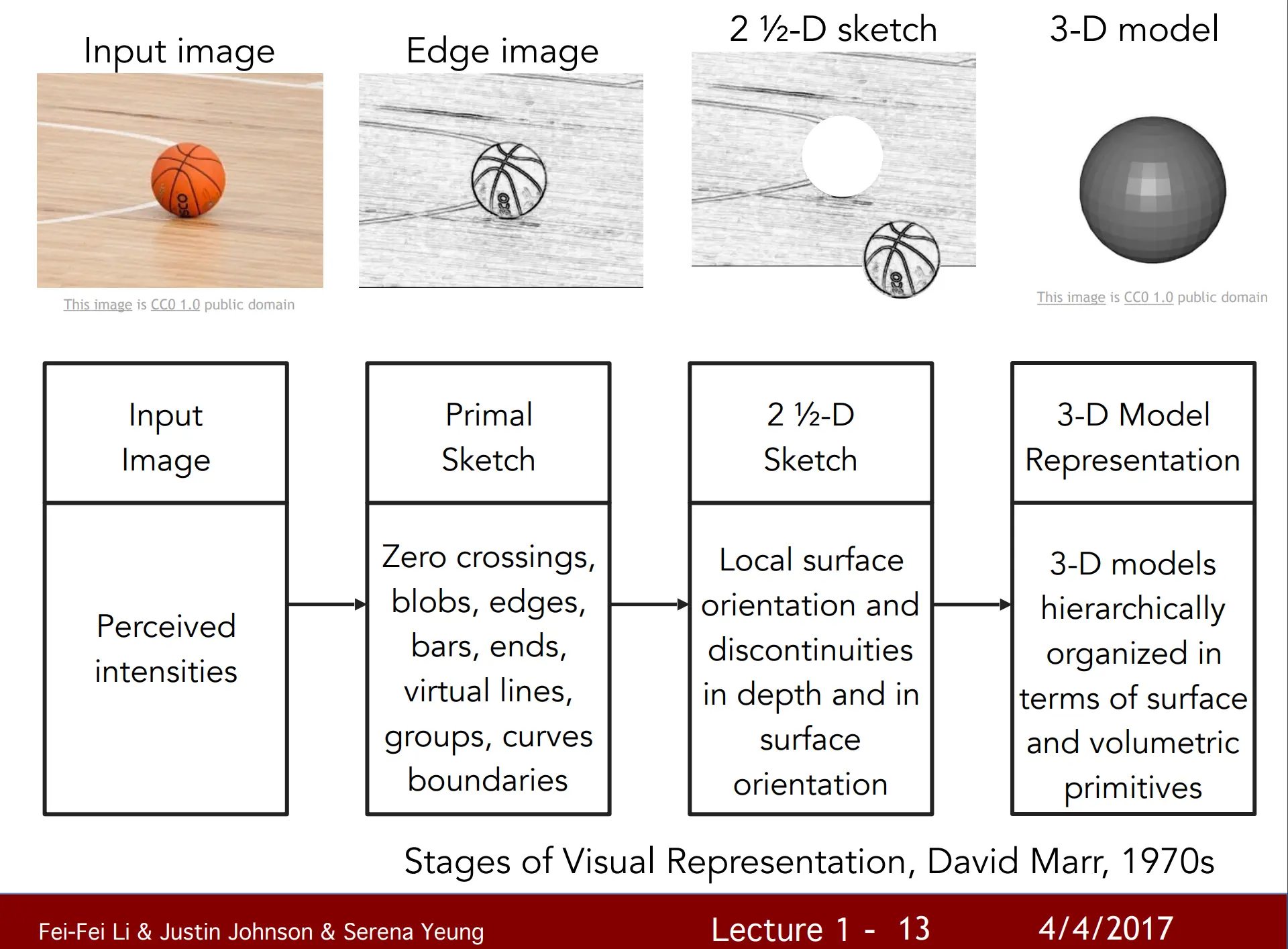
Short Description: A classic, comprehensive guide to deep learning for computer vision, presented by Stanford.
Details:
- Platform: YouTube
- Pricing: Free
- Level: Intermediate to Advanced
- Projects/Assignments: Yes
- Duration: Self-paced
Stanford’s CS231n, Deep Learning for Computer Vision, is offered to Stanford students and was made available on YouTube in 2017. This course is often regarded as a classic in computer vision, providing a thorough exploration of deep learning for CV applications. A strong foundation in mathematics, machine learning, and algorithms is recommended. It is best suited to those who have experience with the practical side of computer vision but want to strengthen their theoretical background.
Pros:
- Deep Knowledge: Offers an extensive examination of CNNs, RNNs, and image classification.
- Assignments: Features challenging assignments that involve implementing algorithms from the ground up.
- Expert Instructors: Taught by PhD-level faculty and supported by adept teaching assistants.
Cons:
- Outdated Content: While it offers a solid foundation, the field has advanced significantly since 2017.
- Prerequisites: Requires strong math, algorithmic, and machine learning skills.
- Lack of Community: As a recorded YouTube series, it lacks a dedicated forum or structured support.
Computer Vision Nanodegree Program by Georgia Tech

Short Description: Georgia Tech’s rigorous Nanodegree program in computer vision, delivered on Udacity.
Details:
- Platform: Udacity
- Pricing: Paid
- Level: Intermediate to Advanced
- Projects/Assignments: Yes
- Duration: 2 months
Despite being a paid program, this Nanodegree is among the best ways to gain qualification for an entry-level computer vision position. It comprises 11 courses and covers the discipline thoroughly with both projects and assignments.
Think of it as a streamlined version of a university-level undergraduate program. You would not solely enroll to learn computer vision; you would also challenge yourself, build upon your knowledge, and demonstrate real-world proficiency in this domain, building portfolios that reflect your practical experience.
Pros:
- Nanodegree: A recognized credential that adds value to your résumé.
- Projects: Balances theoretical knowledge with practical, hands-on work.
- Mentorship: Provides mentorship and career support.
- Excellent Instructors: World-class faculty with extensive experience.
Cons:
- Pricing: The expense may be a limiting factor for some learners.
- Prerequisites: Requires a background in coding, mathematics, and algorithms.
- Experience: Assumes previous working experience in computer vision applications.
Conclusion
Computer vision is one of today’s most rapidly expanding fields. New developments are reshaping entire industries and opening up unprecedented opportunities for professionals. Now is an excellent time to begin your computer vision journey.
We have assembled a list of five courses and programs. Which one you select depends on your background, aspirations, and budget. Whether you are exploring computer vision in smaller personal projects or diving into ML datasets for enterprise solutions, a solid learning path will help you master the fundamentals and keep pace with the latest innovations.
Explore More
- What is Computer Vision Anyway? [Updated 2026]
- Top 5 Open-Source Computer Vision Models of 2026
- Data Annotation with a Human in-the-loop
References
- Unitlab Blog
- Fortune Business Insights: Computer Vision Market Size
- YouTube: Deep Learning for Computer Vision
- fast.ai: Practical Deep Learning for Coders
- Coursera: Introduction to Computer Vision and Image Processing
- YouTube: Convulational Neural Networks for Visual Recognition
- Udacity: Computer Vision
- Roboflow: Best Computer Vision Courses [2025]

![What is Computer Vision Anyway? [Updated 2026]](/content/images/size/w360/2026/01/CV-Essentials.png)
